第二部分:自定義布局管理器
在java.awt包與javax.swing包下有許多現成的布局類,比如BorderLayout、FlowLayout,還有較為復雜的、用于精確定位的布局類GridBagLayout、SpringLayout等。起初我剛剛從事gooey時(06年中),企圖依靠JDK自帶的布局類進行布局,但是實際不可能或者說很難做到。對于復雜的GridBagLayout、SpringLayout來說又望而生畏,而且使用GridBagLayout、SpringLayout來完成布局的話工作量相當可觀,因此當時放棄了布局管理器,采用ComponentListener等尺寸監聽事件來布局組件。雖然這種做法沒有工具支持、采用手工coding,但是自由度上升了很多,而且熟悉了以后編碼效率也大幅其高。與此同時,我開始接觸SWT,發現org.eclipse.swt.layout.FormLayout布局很強大、用起來愛不釋手、要多好有多好、要多強有多強......。于是當時我用來布局組件的方式是采用ComponentListener監聽與FormLayout結合的方式,也是在同期,我領悟到了九宮圖這種專業布局,因此之后九宮圖的實現也都采用上述兩種方法。隨著對SWT的不斷了解外加IM軟件界面的專業性,我發現SWT并不非常適合做專業外觀,也因為此我逐漸將精力轉向Swing。
在介紹如何編寫自定義布局管理器前,我想先把SWT體系下的FormLayout布局(表單布局)特點做個簡要介紹。
SWT體系下的FormLayout是非常靈活、精確的布局,FormLayout布局組件的特點是采用百分比+偏移量的方式。前者可以應付容器尺寸變化時內部組件隨之等比例調整;后者以應付精確的布局。這一特征是通過org.eclipse.swt.layout.FormData和org.eclipse.swt.layout.FormAttachment兩個類來實現。
通常使用FormLayout來定位一個組件要確定4個FormAttachment對象:top、bottom、left、right,即組件的4條邊。而且通常是使用FormAttachment(int numerator,int offset)這個構造器,也就是百分比+偏移量。當然FormAttachment不只這一種,但是都是可選的,如果想深入研究FormLayout可以參閱SWT相關的介紹。
下面給出一段SWT示例程序:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Display display = new Display();
Shell shell = new Shell(display);
shell.setText("SWT Application");
shell.setLayout(new FormLayout());
final Button button = new Button(shell, SWT.NONE);
button.setText("button");
final FormData formData = new FormData();
formData.top = new FormAttachment(20, 0);
formData.left = new FormAttachment(50, 0);
formData.bottom = new FormAttachment(20, 30);
formData.right = new FormAttachment(50, 50);
button.setLayoutData(formData);
shell.open();
while (!shell.isDisposed()) {
if (!display.readAndDispatch()) {
display.sleep();
}
}
display.dispose();
}
運行效果如下:
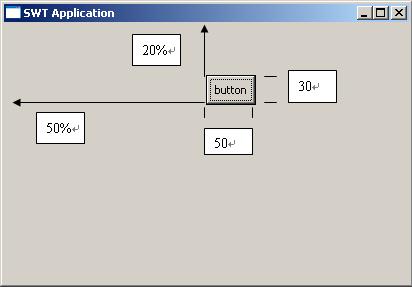
由運行效果可以看出,FormLayout通過指定組件的四條邊來完成布局。
FormLayout很強大、靈活,但是AWT、Swing包中卻沒有,但是不等于說不能實現,學習了上文之后當然可以移植到Swing中來。
SWT中使用FormLayout還要結合FormData(表單數據)與FormAttachment(表單附件)。下面給出這兩個移植過來的類實現
public final class FormAttachment {
float percentage; // 這個參數與SWT中的不同,不叫numerator,而是其等價的小數形式
int offset;
public FormAttachment(float percentage, int offset) {
this.percentage = percentage;
this.offset = offset;
}
}
public final class FormData {
public FormAttachment left;
public FormAttachment right;
public FormAttachment top;
public FormAttachment bottom;
}
你應該了解坐標系的概念,Java中的坐標系以向右、向下為正方向。因此對于offset,正值是向右、向下偏移;負值是向左、向上偏移。
與SWT的FormAttachment稍有不同的是,我自定義的構造器第一個參數是float類型,它代表的意思與“FormAttachment(int numerator,int offset)”相同,都是表示百分比,只不過前者用整數表示,后者用小數表示。例如SWT中“new FormAttachment(20,0);”用后者表示就是“new FormAttachment(0.2f,0);”。
在FormLayout布局中,定位一個組件需要最多4個FormAttachment對象,但是可以不必全部指定,稍后可以看到缺省的行為。
如果你的布局管理器比較簡單,可以實現LayoutManager接口。但是正如上文所述,LayoutManager的addLayoutComponent(String name, Component comp)方法是必須通過java.awt.Container類的“Component add(String name, Component comp)”方法觸發調用,其中的字符串參數指定了布局信息。但是字符串表達方式很有限,因此應當采用LayoutManager2接口,這樣,addLayoutComponent(Component comp, Object constraints)方法被調用時,“Object constraints”可以是任何類型的對象,很方便。下面逐步實現這個類。
首先搭建的原型如下
public final class FormLayout implements LayoutManager2 {
public void addLayoutComponent(Component comp, Object constraints) {}
public float getLayoutAlignmentX(Container target) {
return 0;
}
public float getLayoutAlignmentY(Container target) {
return 0;
}
public void invalidateLayout(Container target) {}
public Dimension maximumLayoutSize(Container target) {
return null;
}
public void addLayoutComponent(String name, Component comp) {}
public void layoutContainer(Container parent) {}
public Dimension minimumLayoutSize(Container parent) {
return null;
}
public Dimension preferredLayoutSize(Container parent) {
return null;
}
public void removeLayoutComponent(Component comp) {}
}
再聲明一個保存組件與布局信息對應關系的映射:private final Map<Component, FormData> componentConstraints = new HashMap<Component, FormData>();
接著完成addLayoutComponent方法的實現。在完成編寫之前我們看一下怎樣去使用FormLayout以做到心中有數。下面的一段代碼是調用FormLayout示例:
getContentPane().setLayout(new FormLayout());
JButton button = new JButton();
button.setText("button");
FormData formData = new FormData();
formData.top = new FormAttachment(0.2f, 0);
formData.left = new FormAttachment(0.5f, 0);
formData.bottom = new FormAttachment(0.2f, 30);
formData.right = new FormAttachment(0.5f, 50);
getContentPane().add(button,formData);
如上所示,當調用“getContentPane().add(button,formData);”時,布局類的 public void addLayoutComponent(Component comp, Object constraints)方法便會調用,constraints參數就是FormData對象。所以在addLayoutComponent方法中需要做的就是把組件與布局信息關聯起來。下面是完整實現:
public void addLayoutComponent(Component comp, Object constraints) {
if (constraints == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("constraints can't be null");
} else if (!(constraints instanceof FormData)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("constraints must be a " + FormData.class.getName() + " instance");
} else {
synchronized (comp.getTreeLock()) {
FormData formData = (FormData) constraints;
if (formData.left == null || formData.top == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("left FormAttachment and top FormAttachment can't be null");
}
componentConstraints.put(comp, (FormData) constraints);
}
}
}
前面的合法性檢查是必需的,你懂的。然后比較重要的就是“synchronized (comp.getTreeLock()) ”,這是保障在多線程的環境下能安全執行,如果你察看JDK源碼布局類的實現,會發現這個同步多次用到,我這么用也是參考JDK的實現。關于getTreeLock的實現在JDK6.0源碼中是這樣實現的。
public abstract class Component implements ImageObserver, MenuContainer, Serializable {
... static final Object LOCK = new AWTTreeLock();
static class AWTTreeLock {}
... public final Object getTreeLock() {
return LOCK;
}
...}
還要注意的是傳入的FormData實例的left、top FormAttachment必須要給出,因為這兩個FormAttachment代表的是Location(位置)信息,因此必須指定。對于right、bottom可以不指定,但是如果不指定的話,必須能從getPreferredSize()中得到信息,否則組件的尺寸將無法確定。
對于addLayoutComponent(String name, Component comp)方法,由于通過查看源碼發現“實現了LayoutManager2 接口的布局類該方法永遠不會被調用”(未來的JDK版本如何實現不能保證),所以該方法空實現,并在注視上作@deprecated標記。
/**
* @deprecated
*/
public void addLayoutComponent(String name, Component comp) {}
除了layoutContainer方法,其余方法均很簡單。一并給出:
public float getLayoutAlignmentX(Container target) {
return 0.5f;
}
public float getLayoutAlignmentY(Container target) {
return 0.5f;
}
public void invalidateLayout(Container target) {}
public Dimension maximumLayoutSize(Container target) {
return new Dimension(Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
} public Dimension minimumLayoutSize(Container target) {
return new Dimension(0, 0);
}
public Dimension preferredLayoutSize(Container target) {
return new Dimension(0, 0);
}
public void removeLayoutComponent(Component comp) {
synchronized (comp.getTreeLock()) {
componentConstraints.remove(comp);
}}
根據
上文所述,這些方法不難理解。其實對于FormLayout來說,...LayoutSize(Container target)、getLayoutAlignmentX等方法不是很重要。重要的是public void layoutContainer(Container target)的實現,也是所有布局類最重要的一個類。
首先該方法的第一步也要套上 synchronized (target.getTreeLock()) {},所有的代碼放入同步塊中。接下來是:
final int w = parent.getWidth();
final int h = parent.getHeight();
final Component[] components = parent.getComponents();
for (final Component comp : components) {}
不難理解,是要首先獲取容器當前的長、高,然后
遍歷容器內的所有組件逐一進行布局。下面的工作就是在for循環體中做文章了。循環體第一段是
final FormData formData = componentConstraints.get(comp);
if (formData == null) {
continue;
}
因為在addLayoutComponent(Component comp, Object constraints)方法中已經關聯了組件與布局信息,所以可以通過componentMap.get(comp)這一行得到組件的布局信息,加上空值判斷確保代碼萬無一失。
接下來取出4個FormAttachment對象,表示組件的四條邊。
final FormAttachment left = formData.left;
final FormAttachment right = formData.right;
final FormAttachment top = formData.top;
final FormAttachment bottom = formData.bottom;
然后計算Location信息(組件左上角的坐標)x、y:
final int x = (int) (left.percentage * w) + left.offset; // 左邊的x坐標
final int y = (int) (top.percentage * h) + top.offset; // 上邊的y坐標
計算方法就是FormLayout的布局方式:(百分比*容器尺寸)+像素偏移量。
然后計算組件的長、高,width、height:
final int width;
final int height;
if (right == null || bottom == null) {
final Dimension size = comp.getPreferredSize();
if (size == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("If right FormAttachment or bottom FormAttachment is null,the component must have preferred-size");
} else {
width = size.width;
height = size.height;
}
} else {
final int x2 = (int) (right.percentage * w) + right.offset; // 右邊的x坐標
final int y2 = (int) (bottom.percentage * h) + bottom.offset; // 下邊的y坐標
width = x2 - x;
height = y2 - y;
}
計算時根據給出right與bottom布局分為兩種情況,如果未給出,那么根據組件的getPreferredSize方法得到組件的最佳大小,以這個大小決定組件的尺寸。作為規范,使用布局管理器布局不是參照組件的getSize而是參照getPreferredSize來最終決定組件的尺寸,所有布局管理器也都是這么實現的。所以如果你企圖
設置組件的setSize()方法來達到在布局管理器中布局的目的是不可能的,所以你應該視圖調用組件的setPreferredSize方法。接上,如果right和bottom都不是null,那么計算組件尺寸將忽略getPreferredSize,計算x2和y2的坐標,然后兩坐標相減得到長寬。最后調用組件的setBounds進行最終定位。
comp.setBounds(x, y, width, height);
可見對于布局管理器,其布局原理與使用絕對布局一樣,調用setBounds實現,沒什么特別之處。只不過是把布局單獨抽出成一個類來實現罷了。
layoutContainer的完整代碼如下:
public void layoutContainer(final Container parent) {
synchronized (parent.getTreeLock()) {
final int w = parent.getWidth();
final int h = parent.getHeight();
final Component[] components = parent.getComponents();
for (final Component comp : components) {
final FormData formData = componentConstraints.get(comp);
if (formData == null) {
continue;
}
final FormAttachment left = formData.left;
final FormAttachment right = formData.right;
final FormAttachment top = formData.top;
final FormAttachment bottom = formData.bottom;
final int x = (int) (left.percentage * w) + left.offset;
final int y = (int) (top.percentage * h) + top.offset;
final int width;
final int height;
if (right == null || bottom == null) {
final Dimension size = comp.getPreferredSize();
if (size == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("If right FormAttachment or bottom FormAttachment is null,the component must have preferred-size");
} else {
width = size.width;
height = size.height;
}
} else {
final int x2 = (int) (right.percentage * w) + right.offset;
final int y2 = (int) (bottom.percentage * h) + bottom.offset;
width = x2 - x;
height = y2 - y;
}
comp.setBounds(x, y, width, height);
}
}
}
作為FormLayout需要補充的是,在進行最終布局“component.setBounds(x, y, width, height);”之前,未進行邏輯判斷,所以x、y可能會超出了容器的范圍而width、height也可能是負值,這都會導致組件“莫名其妙”地不可見,這都不是布局管理器的問題。例如以下兩行代碼:
formData.left = new FormAttachment(0.5f, 30);
formData.right = new FormAttachment(0.5f, 20);
就會使組件永遠不能顯示,因為對于left的定位,是位于容器50%處向右30像素處,而right是位于容器50%處向右20像素處,這樣組件的長度就是-10,怎么能顯示出來呢?
FormLayout就介紹到這里,因為發帖只能在周末,加上最近一段時間還有別的事,能擠出一點時間真不容易。請關注下一篇CenterLayout的實現。