正統的學習筆記沒有記,為什么?提醒自己,spring你是學過的,這次復習,只是把要點記下來就可以了,也是為什么只看spring in action的原因:
Spring基礎學習注記
Spring是輕量級的,AOP的,DI的,框架的,容器的
輕量級:體積(2.5M),開銷
DI:通過DI來松耦。所謂依賴注入,即組件之間的依賴關系由容器在運行期決定,形象的來說,即由容器動態的將某種依賴關系注入到組件之中
AOP:理解為“切面”比較合適,AOP則是針對業務處理過程中的切面進行提取,它所面對的是處理過程中的某個步驟或階段,以獲得邏輯過程中各部分之間低耦合性的隔離效果。OOD/OOP面向名詞領域,AOP面向動詞領域。AOP還有另外一個重要特點:源碼組成無關性。
容器的:負責AO的lifecycle和configuration。可以定義AO如何被創建、如何配置和如何相互關聯。
框架:配置和組合應用,管理AO,通過XML配置,并提供很多基礎設施服務,比如事務管理,持久化框架集成。
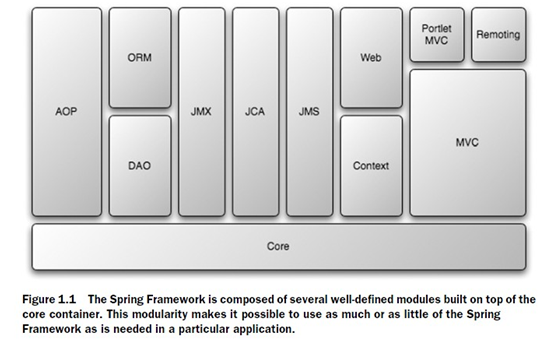
Spring’s core container:提供基本功能,包括BeanFactory(DI的基礎,spring框架的基礎)。
Application context module:core使spring像個容器,而context則使其像一個框架。常用的一個應用就是集成velocity和freemarker的一個集成點。
Spring’s AOP module:顧名思義。
JDBC abstraction and the DAO module:集成數據庫操作。這個模塊會利用AOP模塊提供的事務管理功能。
Object-relational mapping (ORM) integration module:在DAO的基礎上提供ORM的solution。Spring不實現自己的ORM,只是提供一個與ORM框架結合的接口,比如Hibernate,JPA,JDO,IBATIS等。同樣spring的事務管理也與這些框架相結合。
Java Management Extensions (JMX):Exposing the inner workings of a Java application for management is a critical part of making an application production ready. Spring’s JMX module makes it easy to expose your application’s beans as JMX MBeans. This makes it possible to monitor and reconfigure a running application.
Java EE Connector API (JCA)
The enterprise application landscape is littered with a mishmash of applications
running on an array of disparate servers and platforms. Integrating these applications
can be tricky. The Java EE Connection API (better known as JCA) provides a
standard way of integrating Java applications with a variety of enterprise information
systems, including mainframes and databases.
In many ways, JCA is much like JDBC, except where JDBC is focused on database
access, JCA is a more general-purpose API connecting to legacy systems. Spring’s
support for JCA is similar to its JDBC support, abstracting away JCA’s boilerplate
code into templates.
The Spring MVC framework
與ORM不同,MVC模塊既結合已有的像Struts、Tapestry、WebWork這樣的框架,也提供了自己的MVC框架。
Spring Portlet MVC
Many web applications are page based—that is, each request to the application
results in a completely new page being displayed. Each page typically presents a
specific piece of information or prompts the user with a specific form. In contrast,
portlet-based applications aggregate several bits of functionality on a single web
page. This provides a view into several applications at once.
If you’re building portlet-enabled applications, you’ll certainly want to look at
Spring’s Portlet MVC framework. Spring Portlet MVC builds on Spring MVC to provide
a set of controllers that support Java’s portlet API.
Spring’s web module
提供MVC模塊需要的classes。
Remoting
Not all applications work alone. Oftentimes, it’s necessary for an application to
leverage the functionality of another application to get its work done. When the
other application is accessed over the network, some form of remoting is used
for communication.
Spring’s remoting support enables you to expose the functionality of your Java
objects as remote objects. Or if you need to access objects remotely, the remoting
module also makes simple work of wiring remote objects into your application as
if they were local POJOs. Several remoting options are available, including
Remote Method Invocation (RMI), Hessian, Burlap, JAX-RPC, and Spring’s own
HTTP Invoker.
Java Message Service (JMS)
The downside to remoting is that it depends on network reliability and that both
ends of the communication be available. Message-oriented communication, on
the other hand, is more reliable and guarantees delivery of messages, even if the
network and endpoints are unreliable.
Spring’s Java Message Service (JMS) module helps you send messages to JMS
message queues and topics. At the same time, this module also helps you create message-driven POJOs that are capable of consuming asynchronous messages.
解釋一個spring的xml:
<beans>是根元素。
<bean>告訴容器如何配置一個class,id屬性表示這個bean對象的名字,class屬性表示這個bean對象的具體class。
<bean>下的<property>用于設置一個該bean對象的屬性property,name屬性表示這個property的名字,value屬性傳遞給這個property值。用property這種方式,等同于利用bean對象的set方法。
<bean>下的<constructor-arg>與<property>類似,只是這個等同于利用bean對象的賦值構造函數。
粗解DI
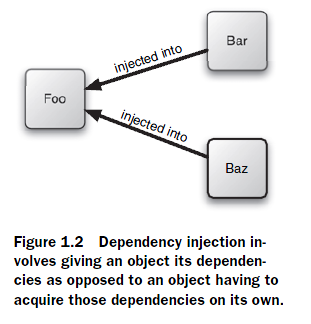
The key benefit of DI is loose coupling.
Interface programming
通過配置文件xml,寫beanfactory等,來實現簡單注入,從而松耦。
粗解AOP
解釋aop的xml配置元素:
<aop:config>解釋要做aop配置,是spring aop基本必備的元素
——<aop:aspect>表示聲明一個aspect,這個aspect的功能被定義在其ref屬性中,ref一般會聯系一個已經定義好的bean對象。一個aspect由pointcuts(功能在哪里實現)和advice(功能怎樣實現)組成。
————<aop:pointcut>定義一個pointcut,觸發條件是某方法被執行。
————<aop:before>顧名思義,一個advice
————<aop:after>同上。
Basic bean wiring
The act of creating these associations between application objects is the
essence of dependency injection (DI) and is commonly referred to as wiring.
Spring container
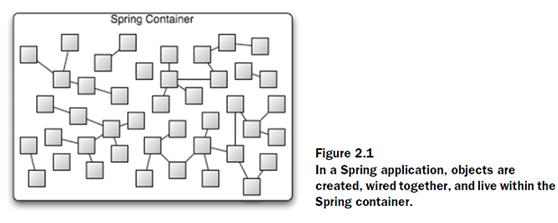
BeanFactory
顧名思義,遵循工廠模式的一個類,管理和分發beans。
通用的工廠,可以管理分發各種類型的beans。
Beanfactory參與了bean的整個生命周期。
多種實現方式,最常用的是org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory,通過加載xml來實現。當然必須要傳遞一個Resource給beanfactory。例:BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(new FileSystemResource("c:/beans.xml"));
得到一個bean的方法就是調用getBean()。比如:MyBean myBean = (MyBean) factory.getBean("myBean");
application context
等同于beanfactory,但是提供more:
1. 支持I18N的消息
2. 提供一般基本方法去加載file resources
3. 發布events到已經注冊為listener的beans
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext和FileSystemXmlApplicationContext比較常用。例:ApplicationContext context = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("c:/foo.xml"); ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("foo.xml");
bean’s life

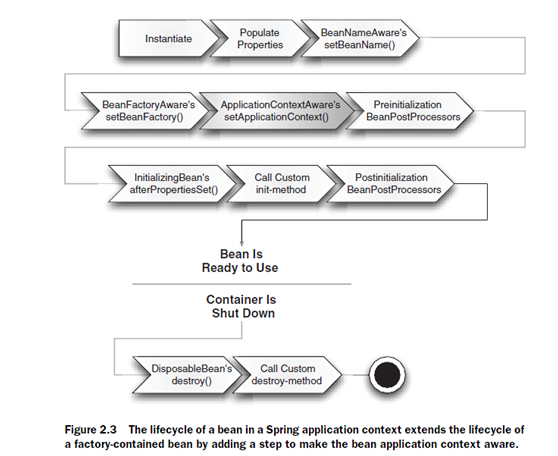
Creating Beans
分兩步,首先聲明一個bean,即定義一個類。然后注入,即為其注入屬性內容。
何時選擇setter注入,何時選擇constructor注入,見spring in action原書第45頁。
Injecting into bean properties
通過<property>元素完成注入。其等價于調用bean對應類的setXXX方法。
例:<property name="song" value="Jingle Bells" />
其中value的值,spring會根據property的具體類別來選擇不同的數據類型。
<property name="instrument" ref="saxophone" />這樣的聲明中,表示該property是一個類的對象,其類就是已經聲明過的某個bean:saxophone。
在<property>下直接定義bean叫做inner bean。(當然通過constructor道理相同)
對于復雜集合類型:
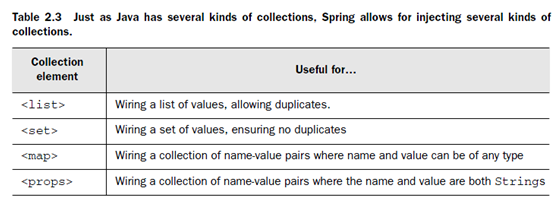
其中的map需要注意一下。Props的代碼實現上與map也不同。
Autowiring
The four types of autowiring
byName:找到name相匹配的,wire
byType:找到type匹配的,wire
constructor:利用constructor參數匹配,wire
autodetect:先constructor,再byType
Controlling bean creation
有多少對象實例,就由多少bean
從靜態的工廠去構造bean,而不是constructor
構造好bean后要及時初始化,在bean銷毀之前要及時clean up
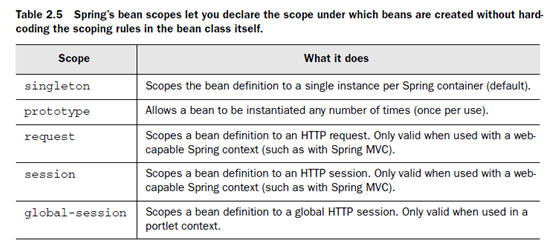
Bean scoping
所有的spring beans都是單例的。
通過設置<bean>的scope=”prototype”,spring可以在需要的時候產生新的bean的實例。
Initializing and destroying beans
<bean>中有init-method和destroy-method負責設置初始化和銷毀時調用的方法。
如果很多bean都有同樣的初始化和銷毀程序,那么可以在<beans>中設置defaultinit-
method 和 default-destroy-method
還有種方法就是bean類的定義時,讓類去實現InitializingBean 和DisposableBean.
Advising beans
重點講述AOP。
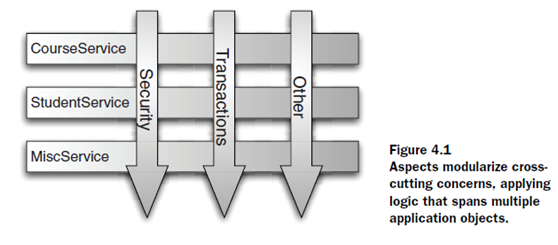
Introducing AOP
Aspect幫助我們建模那些cross-cutting concerns(一個應用中在多個位置起到作用的點,比如security)。
Defining AOP terminology
AOP一般用advice、pointcut和joinpoint描述。
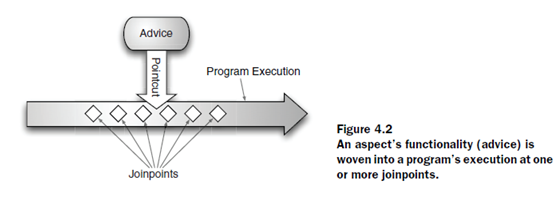
Advice:aspect必定是在做一個job,即要做某個功能。其中這個job就叫做advice。Advice定義了aspect的what和when。
Joinpoint:在整個application中有可能用到advice的連接點。
Pointcut:定義了aspect的where。
Aspect:是advice和pointcut的merger。
Spring’s AOP support
Spring支持4種風格的aop:
Spring的advice都是java寫的。
Spring在運行時advise object。
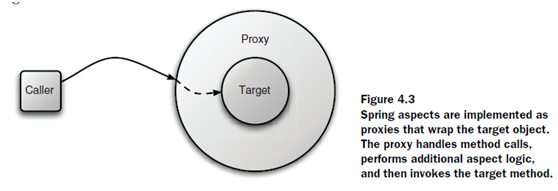
Spring只支持方法連接點method joinpoint。
Spring MVC
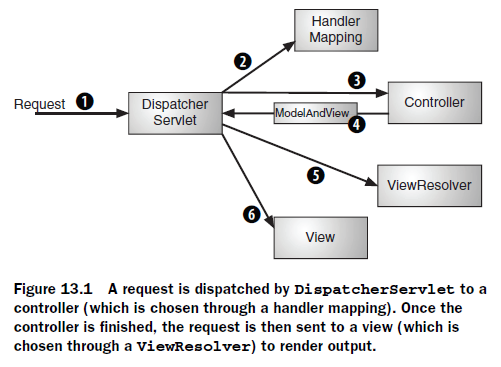
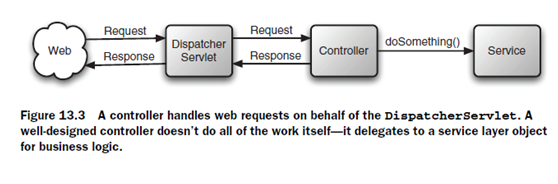
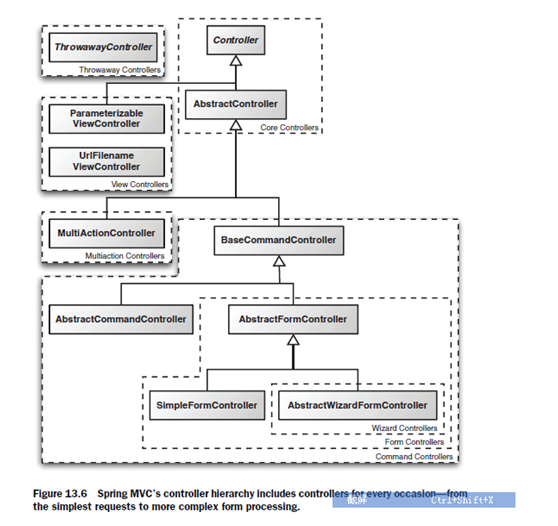
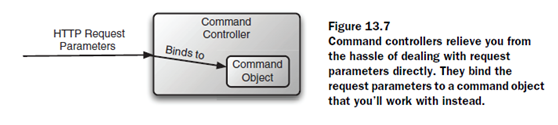
其中,一個command object 就是一個像struts中的actionform一樣的東西。
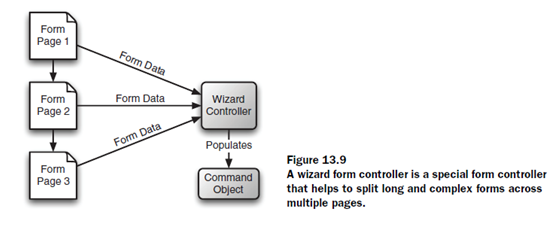
Wizard是一個可以將多個頁面聯合起來作為一個form的東西。
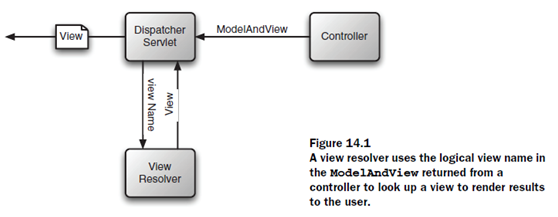
基本搞完了,總的來講,學習的東西就要經常用,否則慢慢的就會淡忘了,尤其是技術上的一些細節。如果沒遇到類似的問題,是很難記憶深刻的~~~