2011年1月11日
#
摘要: 一個(gè)完整的自動(dòng)化測(cè)試框架體系包含以下幾個(gè)部分:1、自動(dòng)化測(cè)試框架;2、測(cè)試腳本以及測(cè)試數(shù)據(jù)管理;3、測(cè)試腳本的執(zhí)行管理系統(tǒng);4、測(cè)試結(jié)果的顯示與分析系統(tǒng)。其中最重要的是自動(dòng)化測(cè)試框架部分。
閱讀全文
摘要: JUnit
JUnit是由 Erich Gamma 和 Kent Beck 編寫(xiě)的一個(gè)回歸測(cè)試框架(regression testing framework)。Junit測(cè)試是程序員測(cè)試,即所謂白盒測(cè)試,因?yàn)槌绦騿T知道被測(cè)試的軟件如何(How)完成功能和完成什么樣(What)的功能。Junit是一套框架,繼承TestCase類(lèi),就可以用Junit進(jìn)行自動(dòng)測(cè)試了。
更多JUnit信息
閱讀全文
摘要: Have you wondered why certain programs are located under /bin, or /sbin, or /usr/bin, or /usr/sbin?
For example, less command is located under /usr/bin directory. Why not /bin, or /sbin, or /usr/sbin? What is the different between all these directories?
In this article, let us review the Linux filesystem structures and understand the meaning of individual high-level directories
閱讀全文
摘要: 當(dāng)今互聯(lián)網(wǎng)的發(fā)展,已不是大魚(yú)吃小魚(yú)的時(shí)代,而是快魚(yú)吃慢魚(yú)的時(shí)代。互聯(lián)網(wǎng)產(chǎn)品的制勝原則就是一個(gè)字——“快”。在各種形態(tài)的產(chǎn)品研發(fā)中,我們始終貫徹如一的價(jià)值觀之一就是“快”,我們應(yīng)該如何來(lái)理解和詮釋“快”?又會(huì)從哪些方面來(lái)執(zhí)行貫徹這個(gè)原則呢?
閱讀全文
摘要: 軟件測(cè)試的十二個(gè)誤區(qū)大體總結(jié)如下:
1) 測(cè)試人員不需要了解軟件開(kāi)發(fā)的知識(shí):
這個(gè)很要命的,我們談到軟件測(cè)試人員未來(lái)的發(fā)展方向大致有:自動(dòng)化測(cè)試,性能測(cè)試,測(cè)試管理,項(xiàng)目經(jīng)理。這其中自動(dòng)化測(cè)試和性能測(cè)試包括項(xiàng)目管理,都會(huì)要求對(duì)軟件開(kāi)發(fā)有深入的理解,如何能設(shè)計(jì)一個(gè)好的自動(dòng)化框架,好的性能測(cè)試用例,如何管理一個(gè)開(kāi)發(fā)團(tuán)隊(duì),這都需要我們?cè)谲浖_(kāi)發(fā)方面有所掌握。不單要掌握,而且要精通。此其一。
其二:如果不了解開(kāi)發(fā)知識(shí),測(cè)試人員很容易被開(kāi)發(fā)人員牽著鼻子走,因?yàn)殚_(kāi)發(fā)人員隨便一忽悠,你如果不了解個(gè)中奧妙,你一個(gè)字也說(shuō)不上來(lái)。(以前我們討論 Cookie和Session,由于GoAhead不支持Session,只能用Cookie來(lái)控制,差點(diǎn)別開(kāi)發(fā)人員忽悠了)
閱讀全文
摘要: 寫(xiě)在前面:寫(xiě)Android程序有一個(gè)很重要的原則,不阻塞UI線程。因此Android提供了5種方法來(lái),讓一些耗時(shí)的作業(yè)在其它線程中執(zhí)行,然后把結(jié)果返回給UI線程,以免阻塞UI線程。
閱讀全文
探討了軟件測(cè)試的可測(cè)試性,主要包括Controllability, Observability, Availability,Simplicity, Stability 和 Information.
HeuristicsOfSoftwareTestability.pdf
摘要: android的selector的用法:
首先android的selector是在drawable/xxx.xml中配置的。
先看一下listview中的狀態(tài):
把下面的XML文件保存成你自己命名的.xml文件(比如list_item_bg.xml),在系統(tǒng)使用時(shí)根據(jù)ListView中的列表項(xiàng)的狀態(tài)來(lái)使用相應(yīng)的背景圖片。drawable/list_item_bg.xml
閱讀全文
摘要: The Monkey is a command-line tool that that you can run on any emulator instance or on a device. It sends a pseudo-random stream of user events into the system, which acts as a stress test on the application software you are developing.
The Monkey includes a number of options, but they break down into four primary categories:
Basic configuration options, such as setting the number of events to attempt.
Operational constraints, such as restricting the test to a single packag
閱讀全文
摘要: Programmers can configure logging either by creating loggers, handlers, and formatters explicitly in a main module with the configuration methods listed above (using Python code), or by creating a logging config file. The following code is an example of configuring a very simple logger, a console handler, and a simple formatter in a Python module:
閱讀全文
摘要: Android系統(tǒng)中Looper負(fù)責(zé)管理線程的消息隊(duì)列和消息循環(huán),具體實(shí)現(xiàn)請(qǐng)參考Looper的源碼。 可以通過(guò)Loop.myLooper()得到當(dāng)前線程的Looper對(duì)象,通過(guò)Loop.getMainLooper()可以獲得當(dāng)前進(jìn)程的主線程的Looper對(duì)象。
閱讀全文
摘要: The list below defines some of the basic terminology of the Android platform.
.apk file
Android application package file. Each Android application is compiled and packaged in a single file that includes all of the application's code (.dex files), resources, assets, and manifest file. The application package file can have any name but must use the .apk extension. For example: myExampleAppname.apk. For convenience, an application package file is often referred to as an ".apk".
Re
閱讀全文
摘要: C.__init__(self[, arg1, ...] )
Constructor (with any optional arguments)
C.__new__(self[, arg1, ...] )[a]
Constructor (with any optional argu ments); usually used for setting up subclassing of immutable data types
C.__del__(self)
Destructor
C.__str__(self)
Printable string representation; str() built-in and print statement
C.__repr__(self)
Evaluatable string representation; repr() built-in and '' operator
閱讀全文
摘要: 本來(lái)這是個(gè)老生常談的問(wèn)題,上周自成又分享了一些性能優(yōu)化的建議,我這里再做一個(gè)全面的Tips整理,謹(jǐn)作為查閱型的文檔,不妥之處,還請(qǐng)指正;
如果你已經(jīng)對(duì)yahoo這些優(yōu)化建議爛熟于心,果斷點(diǎn)這里
閱讀全文
Five test auomation framework are discussed in this paper.
1) The Test Script Modularity Framework
2) The Test Library Architecture Framework
3) The Keyword-Driven or Table-Driven Testing Framework
4) The Data-Driven Testing Framework
5) The Hybrid Test Automation
摘要: 一、ASE(Android Scripting Environment)為Android系統(tǒng)帶來(lái)了腳本語(yǔ)言的技術(shù),通過(guò)它我們可以編輯和執(zhí)行腳本,和腳本解釋交互。腳本可以訪問(wèn)多數(shù)Android API,目前有一個(gè)開(kāi)源項(xiàng)目叫做Scripting Layer for Android (SL4A) ,提供了對(duì)python,javaScript, Lua等腳本的支持。ASE主要通過(guò)兩種方式來(lái)訪問(wèn) Android API,一種是通過(guò)JSON-RPC來(lái)訪問(wèn),另外一種通過(guò)BeanShell(Java語(yǔ)言的動(dòng)態(tài)版本)直接訪問(wèn)Android API。SL4AL架構(gòu)如下圖:
閱讀全文
摘要: 2.你需要學(xué)習(xí)JAVA語(yǔ)言的基礎(chǔ)知識(shí)以及它的核心類(lèi)庫(kù) (collections,serialization,streams,networking, multithreading,reflection,event,handling,NIO,localization,以及其他)。
閱讀全文
1)
http://www.pythonchallenge.com/ 提供了不同level的Python題目,非常有趣的題目。做完一題后,把URL中的pc改為pcc可以看到上一題的答案
2)
http://projecteuler.net/ 里面有200多道題目,不要要求提交代碼,只要最終答案,提供用各種語(yǔ)言來(lái)解決問(wèn)題。這里(
http://dcy.is-programmer.com/posts/8750.html)有部分題目的答案
非常好玩,有興趣的朋友,快來(lái)試試吧
看看 project euler 的第一道題:
If we list all the natural numbers below 10 that are multiples of 3 or 5, we get 3, 5, 6 and 9. The sum of these multiples is 23. Find the sum of all the multiples of 3 or 5 below 1000.
用 python 語(yǔ)言寫(xiě)出來(lái)是:
 print sum(i for i in xrange(1, 1000) if i % 3 == 0 or i % 5 == 0)
print sum(i for i in xrange(1, 1000) if i % 3 == 0 or i % 5 == 0)
This is the first edition of what is expected to become a recurring series on InfoQ. The idea behind this minibook is that a number of InfoQ articles and interviews which deal with a particular topic (in this case, REpresentational State Transfer, or REST) are combined together to provide a detailed exploration suitable for both beginners and advanced practitioners.
Read More: http://www.infoq.com/minibooks/emag-03-2010-rest;jsessionid=1E2375E822D980824403DAD46588FAFE
摘要: #Trie Tree的基本特點(diǎn)
1)根節(jié)點(diǎn)不包含字符,除根節(jié)點(diǎn)外每個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)只包含一個(gè)字符
2)從根節(jié)點(diǎn)到某一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn),路徑上經(jīng)過(guò)的字符連接起來(lái),為該節(jié)點(diǎn)對(duì)應(yīng)的字符串
3)每個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)的所有子節(jié)點(diǎn)包含的字符串不相同
閱讀全文
摘要: The Bloom filter, conceived by Burton Howard Bloom in 1970, is a space-efficient probabilistic data structure that is used to test whether an element is a member of a set.False positivesare possible, but false negatives are not. Elements can be added to the set, but not removed (though this can be addressed with a counting filter). The more elements that are added to the set, the larger the probability of false positives
閱讀全文
摘要: These posts have garnered a number of interesting comments. I want to address two of the negative ones in this post. Both are of the same general opinion that I am abandoning testers and that Google is not a nice place to ply this trade. I am puzzled by these comments because nothing could be further from the truth. One such negative comment I can take as a one-off but two smart people (hey they are reading this blog, right?) having this impression requires a rebuttal. Here are the comments:
閱讀全文
摘要: One of the key ways Google achieves good results with fewer testers than many companies is that we rarely attempt to ship a large set of features at once. In fact, the exact opposite is often the goal: build the core of a product and release it the moment it is useful to as large a crowd as feasible, then get their feedback and iterate. This is what we did with Gmail, a product that kept its beta tag for four years. That tag was our warning to users that it was still being perfected. We removed
閱讀全文
摘要: Lots of questions in the comments to the last two posts. I am not ignoring them. Hopefully many of them will be answered here and in following posts. I am just getting started on this topic.
閱讀全文
摘要: Android applications are, at least on the T-Mobile G1, limited to 16 MB of heap. It's both a lot of memory for a phone and yet very little for what some developers want to achieve. Even if you do not plan on using all of this memory, you should use as little as possible to let other applications run without getting them killed. The more applications Android can keep in memory, the faster it will be for the user to switch between his apps. As part of my job, I ran into memory leaks issues in Andr
閱讀全文
摘要: The Java community is now swamped with discussions about Oracle's patent suit against Google's Android platform. I've been contributing my opinion in several places, but there is one critical topic that needs repeating the same comments everywhere... so, this blog spills the beans once and completely.
閱讀全文
摘要: Activities in the system are managed as an activity stack. When a new activity is started, it is placed on the top of the stack and becomes the running activity -- the previous activity always remains below it in the stack, and will not come to the foreground again until the new activity exits.
閱讀全文
摘要: The one question I get more than any other is "How does Google test?" It's been explained in bits and pieces on this blog but the explanation is due an update
閱讀全文
摘要: Dependency injection asks us to separate the new operators from the application logic. This separation forces your code to have factories which are responsible for wiring your application together. However, better than writing factories, we want to use automatic dependency injection such as GUICE to do the wiring for us. But can DI really save us from all of the new operators?
閱讀全文
摘要: Everyone seems to think that they are writing OO after all they are using OO languages such as Java, Python or Ruby. But if you exam the code it is often procedural in nature
閱讀全文
By James Whittaker
I’ve had a number of questions about the SET role and it seems I have confused folks when I say that the SWE is a tester and the SET is a tester and at the same time the SWE is a developer and the SET is a developer. What could possibly be confusing about that?
Oh, yeah. Right.
My next series of posts are going to detail the role of the SET and all will eventually be clear but some clarification on career path seems worthwhile.
SETs are developers who write test code and automation as their primary task. They are in every sense of the word a developer. When we interview SETs, SWEs are on the interview loop and SWE questions are asked. They are not all of the interview, but they are part of it.
This means that the skill set that our SETs possess makes them perfect candidates for switching to the SWE role. There is neither incentive nor deterrent to do so. SETs and SWEs are on the same pay scale and bonus structure (I have both roles reporting to me so I have real visibility into salary data) and their promotion velocity (again based on actual data) is roughly equivalent. This means that SETs have no outside influences to prompt them one way or the other.
The key factor is really the type of work you are doing. SETs who find themselves involved in SWE work usually convert to SWE. SWEs are also drawn in the opposite direction. Much of this happens through our 20% time work. Any SET interested in SWE work can take on a 20% task doing feature development. Any SWE interested in automation can find a group and sign up for a 20%. Right now I have both SWEs and SETs involved in such cross pollination.
The ideal situation is that the title reflects the actual work that you are involved in. So if an SET starts doing more feature dev work than automation, he or she should convert, same for SWEs doing automation work. In my time here, conversions in both directions have happened, but it is not all that common. The work of both roles is engaging, interesting and intense. Few Googlers are walking around bored.
Bottom line: do the work you are passionate about and capable of and the right job title will find you.
一、概念
靜態(tài)分派(Static Dispatch),發(fā)生在編譯時(shí)期,分派是根據(jù)靜態(tài)類(lèi)型信息發(fā)生的,方法重載就是靜態(tài)分派。
動(dòng)態(tài)分派(Dynamic Dispatch),發(fā)生在運(yùn)行時(shí)期,動(dòng)態(tài)分派動(dòng)態(tài)地置換掉某個(gè)方法。面向?qū)ο蟮恼Z(yǔ)言用動(dòng)態(tài)分派實(shí)現(xiàn)多態(tài)性。
Java語(yǔ)言支持靜態(tài)多分派和動(dòng)態(tài)的單分派,利用設(shè)計(jì)模式Java可以實(shí)現(xiàn)Double Dispatch,即訪問(wèn)者模式。
二、Visitor Pattern
目的:封裝一些施加于某種數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)元素之上的操作。
UML圖:
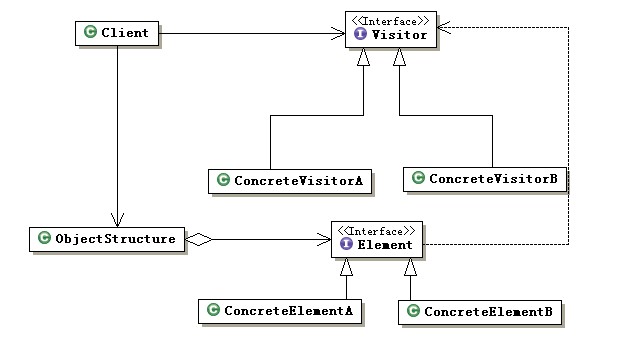
主要原理:“反傳球”,Element來(lái)Visitor之間二輪調(diào)用,調(diào)用過(guò)程中用sinlge dispatch確定類(lèi)型
記錄關(guān)于REST的一些技術(shù):
1、REST簡(jiǎn)介:http://zh.wikipedia.org/zh/REST
2、InfoQ 深入淺出REST: http://www.infoq.com/cn/articles/rest-introduction
摘要: 要設(shè)計(jì)良好的架構(gòu),必須做到關(guān)注點(diǎn)分離,這樣可以產(chǎn)生高內(nèi)聚、低耦合的系統(tǒng),這是美麗架構(gòu)的終極原則
閱讀全文
摘要: A synchronization aid that allows a set of threads to all wait for each other to reach a common barrier point. CyclicBarriers are useful in programs involving a fixed sized party of threads that must occasionally wait for each other. The barrier is called cyclic because it can be re-used after the waiting threads are released.
閱讀全文
摘要: A java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch is a concurrency construct that allows one or more threads to wait for a given set of operations to complete
閱讀全文
文章描述了實(shí)現(xiàn) Multithreaded Servers的3種方法:
1)單線程,性能性差,請(qǐng)求等待時(shí)間長(zhǎng)
2)多線程,把接受請(qǐng)求和處理請(qǐng)求的線程分開(kāi),接受后交給 worker處理
3)線程池,性能最佳,有效地防止負(fù)載過(guò)重,重復(fù)利用線程,請(qǐng)求多時(shí),讓請(qǐng)求排隊(duì)接收處理
4)主要用socket來(lái)通信, ServerSocket 和 Socket
具體文章請(qǐng)看:http://tutorials.jenkov.com/java-multithreaded-servers/index.html
摘要: 軟件模塊之間總是存在著一定的接口,從調(diào)用方式上,可以把他們分為三類(lèi):同步調(diào)用、回調(diào)和異步調(diào)用。
同步調(diào)用是一種阻塞式調(diào)用,調(diào)用方要等待對(duì)方執(zhí)行完畢才返回,它是一種單向調(diào)用,如HTTP;
回調(diào)是一種雙向調(diào)用模式,也就是說(shuō),被調(diào)用方在接口被調(diào)用時(shí)也會(huì)調(diào)用對(duì)方的接口;
異步調(diào)用是一種類(lèi)似消息或事件的機(jī)制,不過(guò)它的調(diào)用方向剛好相反,接口的服務(wù)在收到某種訊息或發(fā)生某種事件時(shí),會(huì)主動(dòng)通知客戶(hù)方(即調(diào)用客戶(hù)方的接口),如JMS;
閱讀全文
摘要: 雖然很少有 Java? 開(kāi)發(fā)人員能夠忽視多線程編程和支持它的 Java 平臺(tái)庫(kù),更少有人有時(shí)間深入研究線程。相反地,我們臨時(shí)學(xué)習(xí)線程,在需要時(shí)向我們的工具箱添加新的技巧和技術(shù)。以這種方式構(gòu)建和運(yùn)行適當(dāng)?shù)膽?yīng)用程序是可行的,但是您可以做的不止這些。理解 Java 編譯器的線程處理特性和 JVM 將有助于您編寫(xiě)更高效、性能更好的 Java 代碼
閱讀全文
The Zen of Python, by Tim Peters
Beautiful is better than ugly.
Explicit is better than implicit.
Simple is better than complex.
Complex is better than complicated.
Flat is better than nested.
Sparse is better than dense.
Readability counts.
Special cases aren't special enough to break the rules.
Although practicality beats purity.
Errors should never pass silently.
Unless explicitly silenced.
In the face of ambiguity, refuse the temptation to guess.
There should be one-- and preferably only one --obvious way to do it.
Although that way may not be obvious at first unless you're Dutch.
Now is better than never.
Although never is often better than *right* now.
If the implementation is hard to explain, it's a bad idea.
If the implementation is easy to explain, it may be a good idea.
Namespaces are one honking great idea -- let's do more of those!
摘要: This is the text of the Commencement address by Steve Jobs, CEO of Apple Computer and of Pixar Animation Studios, delivered on June 12, 2005.
I am honored to be with you today at your commencement from one of the finest universities in the world. I never graduated from college. Truth be told, this is the closest I’ve ever gotten to a college graduation. Today I want to tell you three stories from my life. That’s it. No big deal. Just three stories.
The first story is about conn
閱讀全文
摘要: 1. 軟件架構(gòu)概述
1.1 什么是軟件架構(gòu)
◎ 軟件架構(gòu)的概念很混亂。如果你問(wèn)五個(gè)不同的人,可能會(huì)得到五種不同的答案。
◎ 軟件架構(gòu)概念主要分為兩大流派:
組成派:軟件架構(gòu) = 組件 + 交互。
決策派:軟件架構(gòu) = 重要決策集。
◎ 組成派和決策派的概念相輔相成。
閱讀全文
摘要: 所謂第一范式(1NF)是指數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)表的每一列都是不可分割的基本數(shù)據(jù)項(xiàng),同一列中不能有多個(gè)值,即實(shí)體中的某個(gè)屬性不能有多個(gè)值或者不能有重復(fù)的屬性。如果出現(xiàn)重復(fù)的屬性,就可能需要定義一個(gè)新的實(shí)體,新的實(shí)體由重復(fù)的屬性構(gòu)成,新實(shí)體與原實(shí)體之間為一對(duì)多關(guān)系。在第一范式(1NF)中表的每一行只包含一個(gè)實(shí)例的信息。簡(jiǎn)而言之,第一范式就是無(wú)重復(fù)的列。
閱讀全文
OS實(shí)時(shí)監(jiān)控工具dstat,整合了vmstat, iostat, ifstat, netstat等常見(jiàn)os監(jiān)控工具的優(yōu)點(diǎn),輸出的結(jié)果簡(jiǎn)單直觀,并且結(jié)果可以保存到csv文件。
dokie@ubuntu:~$ dstat
----total-cpu-usage---- -dsk/total- -net/total- ---paging-- ---system--
usr sys idl wai hiq siq| read writ| recv send| in out | int csw
14 5 78 3 0 0| 553k 109k| 0 0 | 83B 989B| 983 2190
8 2 90 0 0 0| 0 0 |2076B 1383B| 0 0 |1076 1407
9 3 89 0 0 0| 0 72k|7530B 420B| 0 0 | 721 1501
9 4 87 0 0 0| 0 0 |9547B 564B| 0 0 | 750 1474
8 2 89 0 0 0| 0 0 | 12k 672B| 0 0 | 772 1681
9 2 89 0 0 0| 0 0 | 13k 792B| 0 0 | 677 1396
dokie@ubuntu:~$ dstat -h
Usage: dstat [-afv] [options..] [delay [count]]
Versatile tool for generating system resource statistics
Dstat options:
-c, --cpu enable cpu stats
-C 0,3,total include cpu0, cpu3 and total
-d, --disk enable disk stats
-D total,hda include hda and total
-g, --page enable page stats
-i, --int enable interrupt stats
-I 5,eth2 include int5 and interrupt used by eth2
-l, --load enable load stats
-m, --mem enable memory stats
-n, --net enable network stats
-N eth1,total include eth1 and total
-p, --proc enable process stats
-r, --io enable io stats (I/O requests completed)
-s, --swap enable swap stats
-S swap1,total include swap1 and total
-t, --time enable time/date output
-T, --epoch enable time counter (seconds since epoch)
-y, --sys enable system stats
--aio enable aio stats
--fs enable fs stats
--ipc enable ipc stats
--lock enable lock stats
--raw enable raw stats
--socket enable socket stats
--tcp enable tcp stats
--udp enable udp stats
--unix enable unix stats
--vm enable vm stats
-M stat1,stat2 enable external plugins
--mods stat1,stat2
--list list all internal and external plugins
-a, --all equals -cdngy (default)
-f, --full expand -C, -D, -I, -N and -S discovery lists
-v, --vmstat equals -pmgdsc -D total
--integer show integer values
--nocolor disable colors (implies --noupdate)
--noheaders disable repetitive headers
--noupdate disable intermediate updates
--output file write CSV output to file
delay is the delay in seconds between each update
count is the number of updates to display before exiting
The default delay is 1 and count is unspecified (unlimited)
常用的命令:dstat -cdlmnpsy
導(dǎo)出為CVS:
dstat -ta --output osstat.csv
1. 安裝JDK
http://wiki.ubuntu.org.cn/Java%E5%AE%89%E8%A3%85%E9%85%8D%E7%BD%AE
2. 安裝Python
1). apt-get install python
2). PyDev for eclipse:
Name:PyDev,Location:http://pydev.org/updates
Ref:http://www.cnblogs.com/Realh/archive/2010/10/10/1847251.html
3. 安裝dstat--性能監(jiān)測(cè)工具
apt-get install dstat
下面是來(lái)自 Taobao QA Team中的安全測(cè)試方面的文章,對(duì)初學(xué)者很有指導(dǎo)意義
安全測(cè)試學(xué)習(xí)筆記系列:
1. http://qa.taobao.com/?p=11352
2.http://qa.taobao.com/?p=11363
3.http://qa.taobao.com/?p=11472
4.http://qa.taobao.com/?p=11479
5.http://qa.taobao.com/?p=11484
------
WEB漏洞攻擊之SQL注入:http://qa.taobao.com/?p=11403
摘要: onabort 當(dāng)用戶(hù)中斷下載圖像時(shí)觸發(fā)。
onactivate 當(dāng)對(duì)象設(shè)置為活動(dòng)元素時(shí)觸發(fā)。
onafterprint 對(duì)象所關(guān)聯(lián)的文檔打印或打印預(yù)覽后立即在對(duì)象上觸發(fā)。
onafterupdate 當(dāng)成功更新數(shù)據(jù)源對(duì)象中的關(guān)聯(lián)對(duì)象后在數(shù)據(jù)綁定對(duì)象上觸發(fā)。
onbeforeactivate new 對(duì)象要被設(shè)置為當(dāng)前元素前立即觸發(fā)。
onbeforecopy 當(dāng)選中區(qū)復(fù)制到系統(tǒng)剪貼板之前在源對(duì)象觸發(fā)。
onbeforecut 當(dāng)選中區(qū)從文檔中刪除之前在源對(duì)象觸發(fā)。
onbeforedeactivate 在 activeElement 從當(dāng)前對(duì)象變?yōu)楦肝臋n其它對(duì)象之前立即觸發(fā)。
onbeforeeditfocus 在包含于可編輯元素內(nèi)的對(duì)象進(jìn)入用戶(hù)界面激活狀態(tài)前或可編輯容器變成控件選中區(qū)前觸發(fā)。
onbeforepaste 在選中區(qū)從系統(tǒng)剪貼板粘貼到文檔前在目標(biāo)對(duì)象上觸發(fā)。
閱讀全文
數(shù)組類(lèi)Array是Java中最基本的一個(gè)存儲(chǔ)結(jié)構(gòu)。它用于存儲(chǔ)一組連續(xù)的對(duì)象或基本類(lèi)型的數(shù)據(jù)。其中的元素的類(lèi)型必須相同。
Array是最有效率的一 種:
1、效率高,但容量固定且無(wú)法動(dòng)態(tài)改變。 Array還有一個(gè)缺點(diǎn)是,無(wú)法判斷其中實(shí)際存有多少元素,length只是告訴我們Array的容量。
2、Java中有一個(gè)Arrays類(lèi),專(zhuān)門(mén)用來(lái)操作Array,提供搜索、排序、復(fù)制等靜態(tài)方法。 equals():比較兩個(gè)Array是否相等,Array擁有相同元素個(gè)數(shù),且所有對(duì)應(yīng)元素兩兩相等。 fill():將值填入Array中。 sort():用來(lái)對(duì)Array進(jìn)行排序。 binarySearch():在排好序的Array中尋找元素。 System.arraycopy():Array的復(fù)制。
Java Collections Framework成員主要包括兩種類(lèi)型,即:Collection和Map類(lèi)型。 在Java中提供了Collection和Map接口。其中List和Set繼承了Collection接口;Vector、ArrayList、 LinkedList三個(gè)類(lèi)實(shí)現(xiàn)List接口,HashSet、TreeSet實(shí)現(xiàn)Set接口,HashTable、HashMap、 TreeMap實(shí)現(xiàn)Map接口。由此可見(jiàn),Java中用8種類(lèi)型的基本數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)來(lái)實(shí)現(xiàn)其Collections Framework;下面分別進(jìn)行介紹。
Vector:基于Array的List,性能也就不可能超越Array,并且Vector是"sychronized"的,這個(gè)也是Vector和ArrayList的唯一的區(qū)別。
ArrayList:同Vector一樣是一個(gè)基于Array的,但是不同的是ArrayList不是同步的。所以在性能上要比Vector優(yōu)越一些,但 是當(dāng)運(yùn)行到多線程環(huán)境中時(shí),可需要自己在管理線程的同步問(wèn)題。從其命名中可以看出它是一種類(lèi)似數(shù)組的形式進(jìn)行存儲(chǔ),因此它的隨機(jī)訪問(wèn)速度極快。
LinkedList:LinkedList不同于前面兩種List,它不是基于Array的,所以不受Array性能的限制。它每一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)(Node) 都包含兩方面的內(nèi)容:
1、節(jié)點(diǎn)本身的數(shù)據(jù)(data);
2、下一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)的信息(nextNode)。所以當(dāng)對(duì)LinkedList做添加,刪除動(dòng)作的時(shí)候 就不用像基于Array的List一樣,必須進(jìn)行大量的數(shù)據(jù)移動(dòng)。只要更改nextNode的相關(guān)信息就可以實(shí)現(xiàn)了所以它適合于進(jìn)行頻繁進(jìn)行插入和刪除操 作。這就是LinkedList的優(yōu)勢(shì)。Iterator只能對(duì)容器進(jìn)行向前遍歷,而 ListIterator則繼承了Iterator的思想,并提供了對(duì)List進(jìn)行雙向遍歷的方法。
List總結(jié):
1、所有的List中只能容納單個(gè)不同類(lèi)型的對(duì)象組成的表,而不是Key-Value鍵值對(duì)。例如:[ tom,1,c ];
2、所有的List中可以有相同的元素,例如Vector中可以有 [ tom,koo,too,koo ];
3、所有的List中可以有null元素,例如[ tom,null,1 ];
4、基于Array的List(Vector,ArrayList)適合查詢(xún),而LinkedList(鏈表)適合添加,刪除操作。
HashSet:雖然Set同List都實(shí)現(xiàn)了Collection接口,但是他們的實(shí)現(xiàn)方式卻大不一樣。List基本上都是以Array為基礎(chǔ)。但是 Set則是在HashMap的基礎(chǔ)上來(lái)實(shí)現(xiàn)的,這個(gè)就是Set和List的根本區(qū)別。HashSet的存儲(chǔ)方式是把HashMap中的Key作為Set的 對(duì)應(yīng)存儲(chǔ)項(xiàng),這也是為什么在Set中不能像在List中一樣有重復(fù)的項(xiàng)的根本原因,因?yàn)?/span>HashMap的key是不能有重復(fù)的。HashSet能快速定位 一個(gè)元素,但是放到HashSet中的對(duì)象需要實(shí)現(xiàn)hashCode()方法0。
TreeSet則將放入其中的元素按序存放,這就要求你放入其中的對(duì)象是可排序的,這就用到了集合框架提供的另外兩個(gè)實(shí)用類(lèi)Comparable和 Comparator。一個(gè)類(lèi)是可排序的,它就應(yīng)該實(shí)現(xiàn)Comparable接口。有時(shí)多個(gè)類(lèi)具有相同的排序算法,那就不需要重復(fù)定義相同的排序算法,只要實(shí)現(xiàn)Comparator接口即可。TreeSet是SortedSet的子類(lèi),它不同于HashSet的根本就是TreeSet是有序的。它是通過(guò)SortedMap來(lái)實(shí)現(xiàn)的。
Set總結(jié):
1、Set實(shí)現(xiàn)的基礎(chǔ)是Map(HashMap);
2、Set中的元素是不能重復(fù)的,如果使用add(Object obj)方法添加已經(jīng)存在的對(duì)象,則會(huì)覆蓋前面的對(duì)象; Set里的元素是不能重復(fù)的,那么用什么方法來(lái)區(qū)分重復(fù)與否呢? 是用==還是equals()? 它們有何區(qū)別? Set里的元素是不能重復(fù)的,即不能包含兩個(gè)元素e1、e2(e1.equals(e2))。那么用iterator()方法來(lái)區(qū)分重復(fù)與否。 equals()是判讀兩個(gè)Set是否相等。==方法決定引用值(句柄)是否指向同一對(duì)象。
HashMap、TreeMap、Hashtable:
1、HashMap也用到了哈希碼的算法,以便快速查找一個(gè)鍵,TreeMap則是對(duì)鍵按序存放,因此它有一些擴(kuò)展的方法,比如 firstKey(),lastKey()等。
2、Hashtable:不允許空(null)鍵(key)或值(value),Hashtable的方法是Synchronize的,在多個(gè)線程訪問(wèn) Hashtable時(shí),不需要自己為它的方法實(shí)現(xiàn)同步,而HashMap 就必須為之提供外同步。 Hashtable和HashMap采用的hash/rehash算法都大概一樣,所以性能不會(huì)有很大的差異。
3、HashMap和Hashtable的區(qū)別:HashMap是Hashtable(線程案例的)的輕量級(jí)實(shí)現(xiàn)(非線程安全的實(shí)現(xiàn)),他們都完成了Map接口。主要區(qū)別在于HashMap允許空(null)鍵(key)或值(value),非同步,由于非線程安全,效率上可能高于Hashtable。
Map總結(jié):
是一種把鍵對(duì)象和值對(duì)象進(jìn)行關(guān)聯(lián)的容器,Map有兩種比較常用的實(shí)現(xiàn): HashTable、HashMap和TreeMap。
摘要: 1005:創(chuàng)建表失敗
1006:創(chuàng)建數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)失敗
1007:數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)已存在,創(chuàng)建數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)失敗
1008:數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)不存在,刪除數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)失敗
1009:不能刪除數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)文件導(dǎo)致刪除數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)失敗
1010:不能刪除數(shù)據(jù)目錄導(dǎo)致刪除數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)失敗
1011:刪除數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)文件失敗
1012:不能讀取系統(tǒng)表中的記錄
1020:記錄已被其他用戶(hù)修改
1021:硬盤(pán)剩余空間不足,請(qǐng)加大硬盤(pán)可用空間...
閱讀全文
摘要: 序言
在擔(dān)任公司高管的幾年間,我面試過(guò)數(shù)以百計(jì)的各個(gè)層面的員工,其中最讓我感到遺憾的一個(gè)現(xiàn)象就是很多人有著非常好的素質(zhì),甚至有的還是名校的畢業(yè)生,因?yàn)椴欢萌ヒ?guī)劃自己的職業(yè),在工作多年后,依然拿著微薄的薪水,為了一份好一點(diǎn)的工作而奔波。很多這樣的人,他們只要稍微修正一下自己的職業(yè)方向,就能夠在職業(yè)發(fā)展上走得更從容。
有一次一個(gè)大連理工大學(xué)的研究生,好像是學(xué)電子的...
閱讀全文
國(guó)外:
BJ Rolison (I.M.Testy) http://blogs.msdn.com/imtesty
BJ是微軟負(fù)責(zé)EE工作的Test Architecture,也是HWTSaM的作者。他的文章非常有條理,看起來(lái)也比較容易,其中的數(shù)據(jù)也非常豐富,是我喜歡的風(fēng)格。
Alan Page http://blogs.msdn.com/alanpa/
Alan是微軟負(fù)責(zé)EE工作的Director,是HWTSaM的主要作者,他的博客是了解微軟測(cè)試非常好的一個(gè)窗口。最近幾年,他不限于測(cè)試技術(shù)的推廣,他更多的考慮是測(cè)試管理,以及測(cè)試氛圍/文化的形成,以及對(duì)于測(cè)試的影響。我很同意他的一句話(huà)“95%的UI自動(dòng)化測(cè)試都是浪費(fèi)時(shí)間”詳情。他的博客文章比較隨意,有時(shí)也不知道他在嘮叨些什么,但不時(shí)卻有很多精彩的觀點(diǎn)。
Google Test Blog http://googletesting.blogspot.com
這是Google官方的測(cè)試博客,信息量很少,除了每年一次的Google Automation Test Conference之外,文章較少。今年6月,James Whittaker離開(kāi)微軟,加入Google后,才到這里增加不少好文章。
James Bach的博客 http://www.satisfice.com/blog/
James是一個(gè)軟件測(cè)試的資深人士,90年代曾在Apple和Boland公司???過(guò)測(cè)試管理工作,后來(lái)在其他一些公司負(fù)責(zé)測(cè)試流程和質(zhì)量管理,2000年自己創(chuàng)辦了satisfice測(cè)試咨詢(xún)公司,提供軟件質(zhì)量保證相關(guān)的咨詢(xún)和培訓(xùn). 他和Cem Kaner撰寫(xiě)了很多Explorary Testing相關(guān)的文章和書(shū)籍,并且提出了Context-Driven-Testing,這些方法論很適合現(xiàn)在的Agile Testing的特點(diǎn)。
Adam Goucher的博客 http://adam.goucher.ca/
一個(gè)多產(chǎn)高質(zhì)的測(cè)試寫(xiě)作專(zhuān)家,基本上每個(gè)月都有10多篇關(guān)于測(cè)試的文章,有時(shí)候一天寫(xiě)了多篇,真是非常佩服他的寫(xiě)作能力。他的思想很有深度,對(duì)軟件測(cè)試各個(gè)方面都有全面的理解,他閱讀了幾乎所有新出的測(cè)試書(shū)籍,并且些了與其相關(guān)的評(píng)論。這些評(píng)論通常非常尖銳。比如說(shuō),HWTSaM的評(píng)論,他的評(píng)論就比較中肯。對(duì)James Whittalkes的 Exploratory Testing評(píng)論 卻是嗤之以鼻。
軟件測(cè)試雜文集:http://blogs.msdn.com/b/cheno/
文章轉(zhuǎn)自:http://www.cesoo.com/
一、寫(xiě)在前面
剛開(kāi)學(xué),趁著有時(shí)間把設(shè)計(jì)模式重新整理一次。學(xué)好設(shè)計(jì)模式是走向架構(gòu)的第一步,系統(tǒng)架構(gòu)應(yīng)該朝著可維護(hù),可擴(kuò)展,強(qiáng)壯性好的方向去發(fā)展。大學(xué)的最后一個(gè)學(xué)期了,時(shí)間不多了,3月初就要去騰訊實(shí)習(xí)了,還有畢設(shè)。加油 :)
二、常見(jiàn)的模式分類(lèi)
|
創(chuàng)建模式
|
結(jié)構(gòu)模式
|
行為模式
|
|
簡(jiǎn)單工廠模式
|
適配器模式
|
不變模式
|
|
工廠方法模式
|
缺省適配模式
|
策略模式
|
|
抽象工廠模式
|
合成模式
|
模版方法模式
|
|
單例模式
|
裝飾模式
|
觀察者模式
|
|
多例模式
|
代理模式
|
迭代子模式
|
|
建造模式
|
享元模式
|
責(zé)任鏈模式
|
|
原始模型模式
|
門(mén)面模式
|
命令模式
|
|
橋梁模式
|
備忘錄模式
|
|
|
狀態(tài)模式
|
|
|
訪問(wèn)者模式
|
|
|
解釋器模式
|
|
|
調(diào)停者模式
|
三、主要模式的定義和描述
以下內(nèi)容來(lái)自《head first 設(shè)計(jì)模式》一書(shū)
|
模式
|
定義
|
描述
|
|
裝飾者
|
動(dòng)態(tài)地將責(zé)任附加到對(duì)象上。若要擴(kuò)展功能,裝飾者提供了比繼承更有彈性的替代方案
|
包裝一個(gè)對(duì)象,以提供新的行為
|
|
狀態(tài)
|
允許對(duì)象在內(nèi)部狀態(tài)改變時(shí)改變它的行為,對(duì)象看起來(lái)好像修改了它的類(lèi)
|
封裝了基本狀態(tài)的行為,并使用委托在行為之間切換
|
|
迭代器
|
提供一種方法順序訪問(wèn)一個(gè)聚合對(duì)象中的各個(gè)元素,而又不暴露其內(nèi)部的表示
|
在對(duì)象的集合之中游走,而不暴露集合的實(shí)現(xiàn)
|
|
外觀(門(mén)面)
|
提供一個(gè)統(tǒng)一的接口,用來(lái)訪問(wèn)子系統(tǒng)中的一群接口。外觀定義了一個(gè)高層接口,讓子系統(tǒng)更多容易使用
|
簡(jiǎn)化一群類(lèi)的接口
|
|
策略
|
定義算法族,分別封裝起來(lái),讓它們之間可以互相替換,此模式讓算法的變化獨(dú)立于使用算法的客戶(hù)
|
封裝可以互換的行為,并使用委托來(lái)決定使用那一種
|
|
代理
|
為另一個(gè)對(duì)象提供一個(gè)替身或點(diǎn)位符以訪問(wèn)這個(gè)對(duì)象
|
包裝對(duì)象,以控制對(duì)此對(duì)象的訪問(wèn)
|
|
工廠方法
|
定義了一個(gè)創(chuàng)建對(duì)象的接口,但由子類(lèi)決定要實(shí)例化的類(lèi)是哪一個(gè)。工廠方法讓類(lèi)把實(shí)例化推遲到子類(lèi)
|
由子類(lèi)決定要?jiǎng)?chuàng)建是具體類(lèi)是哪一個(gè)
|
|
抽象工廠
|
提供一個(gè)接口,用于創(chuàng)建相關(guān)或依賴(lài)對(duì)象的家族,而不需要明確指定具體類(lèi)
|
允許客戶(hù)創(chuàng)建對(duì)象的家族,而無(wú)需指定他們的具體類(lèi)
|
|
適配器
|
將一個(gè)類(lèi)的接口,轉(zhuǎn)換成客戶(hù)期望另一個(gè)接口。適配器讓原來(lái)不兼容的類(lèi)可以合作無(wú)間
|
封裝對(duì)象,并提供不同的接口
|
|
觀察者
|
在對(duì)象之間定義一對(duì)多的依賴(lài),這樣一來(lái),當(dāng)一個(gè)對(duì)象改變時(shí),依賴(lài)它的對(duì)象都會(huì)收到通知并自動(dòng)更新
|
讓對(duì)象能夠在狀態(tài)改變時(shí)被通知
|
|
模板方法
|
在一個(gè)方法中定義一個(gè)算法的骨架,而將一些步驟延遲到子類(lèi)中。模板方法使得子類(lèi)可以在不改變算法結(jié)構(gòu)的情況下,重新定義算法中的某些步驟
|
由子類(lèi)決定如何實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)算法中的步驟
|
|
組合
|
允許你將對(duì)象組成樹(shù)結(jié)構(gòu)來(lái)表現(xiàn)“整體/部分”的層次結(jié)構(gòu)。組合能讓客戶(hù)以一致的方式處理個(gè)別對(duì)象和對(duì)象組合
|
客戶(hù)用一致的方式處理對(duì)象集合和單個(gè)對(duì)象
|
|
單件(單體)
|
確保一個(gè)類(lèi)只有一個(gè)實(shí)例,并提供全局訪問(wèn)點(diǎn)
|
確保只有一個(gè)對(duì)象被創(chuàng)建
|
|
命令
|
將請(qǐng)求封裝成對(duì)象,這可以讓你使用不同的請(qǐng)求、隊(duì)列,或者日志請(qǐng)求來(lái)參數(shù)化其它對(duì)象。命令模式也可以支持撤銷(xiāo)操作
|
封裝請(qǐng)求為對(duì)象
|
四、參考資料
IBM社區(qū)設(shè)計(jì)模式方面資料: http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/design/
常見(jiàn)OO原則:http://m.tkk7.com/jicheng687/archive/2011/02/13/344174.html
--END--
今天無(wú)意中看到InfoQ(http://www.infoq.com/cn/architect)這個(gè)網(wǎng)站,里面的內(nèi)容很不錯(cuò),介紹的內(nèi)容算是國(guó)內(nèi)最先進(jìn)的的,有興趣的朋友可以看看
一、觀察者模式定義
觀察者模式(Observer): 在對(duì)象之間定義一對(duì)多的依賴(lài),這樣一來(lái),當(dāng)一個(gè)對(duì)象改變狀態(tài),依賴(lài)它的對(duì)象都會(huì)收到通知,并自動(dòng)更新
二、在JUnit中的體現(xiàn)
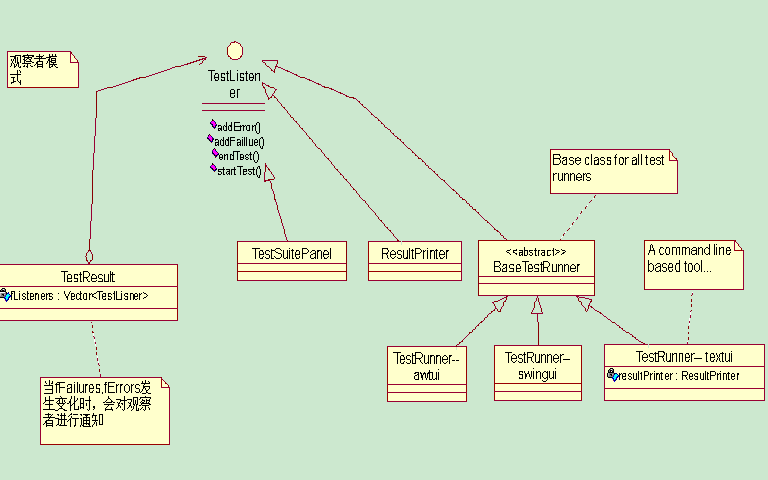
TestResult中用Vector保存各個(gè)監(jiān)聽(tīng)器(文本界面、圖形界面和Eclipse插件)
 protected Vector fListeners; //監(jiān)聽(tīng)器集合
protected Vector fListeners; //監(jiān)聽(tīng)器集合
在測(cè)試運(yùn)行階段,如果出現(xiàn)Error 或者 Failure,TestResult 則會(huì)通知各個(gè)監(jiān)聽(tīng)器

 public synchronized void addFailure(Test test, AssertionFailedError t)
public synchronized void addFailure(Test test, AssertionFailedError t)  {
{
 fFailures.addElement(new TestFailure(test, t));
fFailures.addElement(new TestFailure(test, t));
 //觀察者模式在這里體現(xiàn)出來(lái)了,當(dāng)fFailures有變化時(shí),馬上通知其它Listeners
//觀察者模式在這里體現(xiàn)出來(lái)了,當(dāng)fFailures有變化時(shí),馬上通知其它Listeners

 for (Enumeration e= cloneListeners().elements(); e.hasMoreElements(); )
for (Enumeration e= cloneListeners().elements(); e.hasMoreElements(); )  {
{
 ((TestListener)e.nextElement()).addFailure(test, t);
((TestListener)e.nextElement()).addFailure(test, t);
 }
}
 }
}
一、在單元測(cè)試領(lǐng)域里,JUnit可以說(shuō)是王者,它不但精致,而且使用方便。最后有些時(shí)間,把JUnit源碼讀讀,順便復(fù)習(xí)下設(shè)計(jì)模式 :)
二、參考文章
在深入看代碼之前,先看下面的文章,對(duì)JUnit有一個(gè)基本的了解后,看代碼會(huì)更有目的性。
JUnit官方網(wǎng)站:http://www.junit.org/
分析 JUnit 框架源代碼: http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-junit-src/
JUnit A cook's tour: http://junit.sourceforge.net/doc/cookstour/cookstour.htm
三、核心架構(gòu)
我分析的源碼的版本是JUnit 3.8.2,這個(gè)版本相對(duì)簡(jiǎn)略,把核心思想表現(xiàn)出來(lái)了,沒(méi)有4.X版本那么多附加的功能
JUnit是一個(gè)模式密集型的框架,主要用組合模式、模樣方法、觀察者模式、參數(shù)收集方法、命令模式、裝飾者模式和適配器模式。其中核心是 前三種
核心類(lèi)之間的關(guān)系
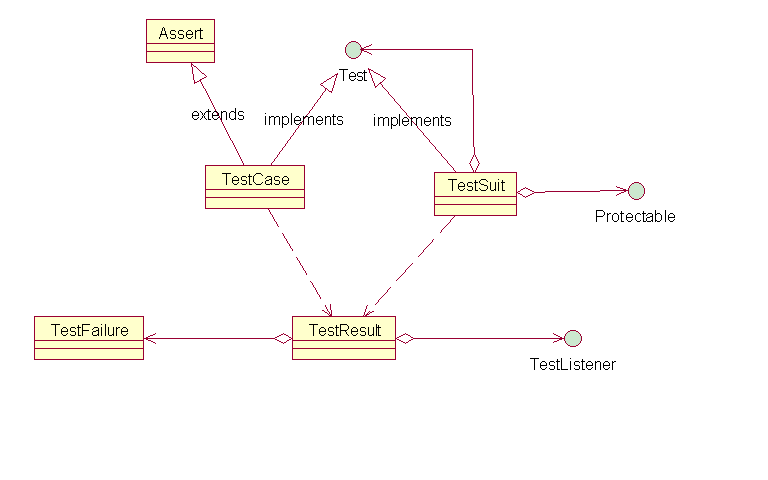
Test、TestCase和TestSuit構(gòu)成了測(cè)試框架的基礎(chǔ),它們用composite模式組合在一起,使得客戶(hù)端可以將對(duì)象的集合以及個(gè)別的對(duì)象(TestCase)一視同仁.TestRusult用來(lái)保存測(cè)試結(jié)果,和TestListner組成observer模式,支持文本界面、圖形界面和 Eclipse 集成組件三種監(jiān)聽(tīng)器
和JUnit A cook's tour中提到的模式圖很相似

類(lèi)與類(lèi)之間的關(guān)系在此就不作解釋了,可以看看參考文章。有興趣的朋友,歡迎一起討論 :)
封裝變化
多用組合,少用繼承
針對(duì)接口編程,不針對(duì)實(shí)現(xiàn)編程
為交互對(duì)象之間的松耦合設(shè)計(jì)而努力
類(lèi)應(yīng)該對(duì)擴(kuò)展開(kāi)放,對(duì)修改關(guān)閉
只和朋友交談
別找我,我會(huì)找你
類(lèi)應(yīng)該只有一個(gè)改變的理由
38、只針對(duì)不正常的條件使用異常
異常只應(yīng)該被用于不正常的條件,它們永遠(yuǎn)不應(yīng)該被用于不正常的條件
設(shè)計(jì)API啟示:一個(gè)良好的API不應(yīng)該強(qiáng)迫它的客戶(hù)為了正常的控制流而使用異常。對(duì)于邊界的判斷常用的有兩種方法:狀態(tài)測(cè)試方法和可被識(shí)別的返回值
40、對(duì)于可以恢復(fù)的條件使用被檢查的異常,對(duì)于程序錯(cuò)誤使用運(yùn)行時(shí)異常
Thowable(可拋出異常)有三種結(jié)構(gòu):被檢查的異常(checked exception)、運(yùn)行時(shí)異常(run-time exception)和錯(cuò)誤(error)
如果期望調(diào)用者能夠恢復(fù),那么,對(duì)于這樣的條件應(yīng)該使用被檢查的異常
運(yùn)行時(shí)異常和錯(cuò)誤,不需要也不應(yīng)該是被捕獲的拋出物
用運(yùn)行時(shí)異常來(lái)指明程序錯(cuò)誤
對(duì)于被檢查的異常,提供一些輔助方法是非常重要的,通過(guò)這些方法,調(diào)用者可以獲得一些有助于恢復(fù)的信息
41、避免不必要地使用被檢查的異常
42、盡量使用標(biāo)準(zhǔn)異常
43、拋出的異常要適合于相應(yīng)的抽象
高層的實(shí)現(xiàn)應(yīng)該捕獲低層的異常,同時(shí)導(dǎo)出一個(gè)可以按照高層抽象進(jìn)行解釋的---異常轉(zhuǎn)譯
低層的異常對(duì)于調(diào)試該異常被撥出的情形非常有幫助的話(huà),可以使用異常鏈接。即低層的異常被高層的異常保存起來(lái),并且高層的異常提供一個(gè)公有的訪問(wèn)方法來(lái)獲得低層異常
44、每個(gè)異常的拋出都必須有文檔
45、在細(xì)節(jié)消息中包含失敗--捕獲信息
為了捕獲失敗,一個(gè)異常的的字符串表示應(yīng)該包含所有“對(duì)異常有貢獻(xiàn)”的參數(shù)和域的值
在異常構(gòu)造函數(shù)中以參數(shù)形式引入這些信息
46、努力使失敗保持原子性
一個(gè)失敗方法調(diào)用應(yīng)該使用對(duì)象保持“它在被調(diào)用之前的狀態(tài)” ---failure atomic
幾種解決方法:在執(zhí)行操作之前檢查參數(shù)的有效性
調(diào)整計(jì)算機(jī)過(guò)程,使得任何可能會(huì)失敗的計(jì)算部分發(fā)生在對(duì)象狀態(tài)被修改之前
編寫(xiě)一段恢復(fù)代碼
在對(duì)象上臨時(shí)都拷貝一份,當(dāng)操作完成之后把臨時(shí)拷貝中的結(jié)果復(fù)制給原來(lái)的對(duì)象。如:Collections.sort
47、不要忽略異常
寫(xiě)上try catch塊
一、二分搜索
二分搜索可以說(shuō)是無(wú)處不在,應(yīng)用它的前提是,對(duì)象有序且在某一范圍之內(nèi)。
二、基本操作的威力
靈機(jī)一動(dòng),經(jīng)過(guò)許久的思考,得出的解決方案或許就是一些基本操作的組合,不是嗎?
求逆代碼:把a(bǔ)b變成ba,可以有如下的方法:ab->a
rb->a
rb
r->(a
rb
r)
r->ba
E.G. n元向量左移i個(gè)位置
 reverse(0, rotdist - 1);
reverse(0, rotdist - 1);
 reverse(rotdist, n-1);
reverse(rotdist, n-1);
 reverse (0, n-1);
reverse (0, n-1);
三、排序
變位分詞的應(yīng)用,關(guān)鍵在于:選擇標(biāo)識(shí)和集中具有相同標(biāo)識(shí)的單詞
四、原理
1)排序:產(chǎn)生有序輸出,將相等的元素集中在一起
2)二分搜索
3)標(biāo)識(shí):當(dāng)使用等價(jià)類(lèi)定義時(shí),定義一種標(biāo)識(shí)使同類(lèi)中每一項(xiàng)都具有相同的標(biāo)識(shí),而該類(lèi)之外的其它項(xiàng)則沒(méi)有該標(biāo)識(shí),這是很有用的
4)問(wèn)題的定義:用戶(hù)的需求才是程序設(shè)計(jì)的根本
5)問(wèn)題解決者的觀點(diǎn):優(yōu)秀的程序員有點(diǎn)懶,他們坐下來(lái)等待靈機(jī)一動(dòng)的出現(xiàn)而不急于使用最開(kāi)始的想法編程