前言
開始花了兩三天的時間學Spring Security�����,還是云山霧罩的�,大受打擊。于是重新總結一下���,飛越迷霧,梳理思路���,寫這樣一篇文字。網上有個雷鋒寫了Spring Security2 學習精講:http://www.javaeye.com/topic/319965里面包含可以運行的代碼�����,如果你對spring scurity感興趣��,可以快速瀏覽一下下面的筆記���,然后debug code����,然后再看看筆記�。Spring Security的內容遠比筆記復雜,我只是根據自己的理解挑重要的記錄并整理一下����。把sample code也當作筆記的一部分���,那個code還是比較精簡地��,更重要的是實用。
官方提供的sample code包居然沒有源代碼�,faint��, google半天找到http://grepcode.com/snapshot/repo1.maven.org/maven2/org.springframework.security/spring-security-samples-contacts/2.0.0 當然���,如果你會用git的話也可以自己check out code, 不過我沒用過git這種高級貨�。
正文
跟權限有關的兩個概念是 認證 和 授權, 先上個圖:
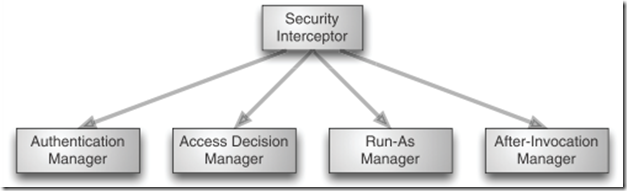
Run-As Manager 和 After-Invocation Manager不重要
The actual implementation of a security interceptor will depend on what resource is being secured. If you’re securing a URL in a web application, the security interceptor will be implemented as a servlet filter. But if you’re securing a method invocation, aspects will be used to enforce security.
這篇只說Authentication Manager:
認證是通過AuthenticationManager來管的�����,
public interface AuthenticationManager {
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
}
The authenticate() method will attempt to authenticate the user using the org.acegisecurity.Authentication object (which carries the principal and credentials). If successful, the authenticate() method returns a complete Authentication object, including information about the user’s granted authorities (which will be considered by the authorization manager).
具體的工作是交給各個 authentication provider來做的:
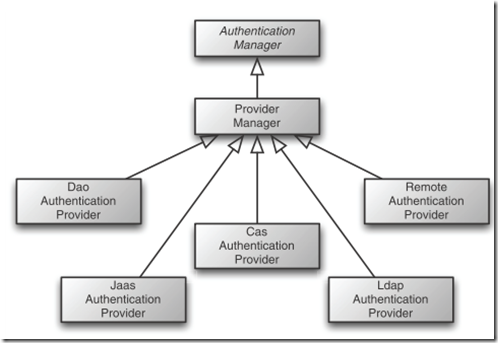
這里provider manager包含多個具體的providers:
<bean id="authenticationManager"
class="org.acegisecurity.providers.ProviderManager">
<property name="providers">
<list>
<ref bean="daoAuthenticationProvider"/>
<ref bean="ldapAuthenticationProvider"/>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
ProviderManager is given its list of authentication providers through its providers property.
以DaoAuthenticationProvider舉例:
<bean id="authenticationProvider"
class="org.acegisecurity.providers.dao.DaoAuthenticationProvider">
<property name="userDetailsService"
ref="userDetailsService"/>
</bean>
它會要求一個UserDetailsService, 跟它相關的是UserDetails接口
UserDetailsService接口是個簡單的接口
public interface UserDetailsService {
UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException, DataAccessException;
}
UserDetails接口如下:
public interface UserDetails extends Serializable {
GrantedAuthority[] getAuthorities();
String getPassword();
String getUsername();
boolean isAccountNonExpired();
boolean isAccountNonLocked();
boolean isCredentialsNonExpired();
boolean isEnabled();
}
解釋一下getAuthorities:該方法返回一個GrantedAuthority[]數組對象�,GrantedAuthority是用戶權限信息對象,這個對象中定義了一個獲取用戶權限描述信息的getAuthority()方法���。
需要注意Authentication對象才是Spring Security使用的進行安全訪問控制用戶信息安全對象。實際上���,Authentication對象有未認證和已認證兩種狀態,在作為參數傳入認證管理器(AuthenticationManager)的authenticate方法時,是一個未認證的對象�,它從客戶端獲取用戶的身份信息(如用戶名���,密碼)����,可以是從一個登錄頁面��,也可以從Cookie中獲取�����,并由系統自動構造成一個Authentication對象。而這里提到的UserDetails代表一個用戶安全信息的源(從數據庫�����,LDAP服務器�,CA中心返回),Spring Security要做的就是將這個未認證的Authentication對象和UserDetails進行匹配��,成功后將UserDetails中的用戶權限信息拷貝到Authentication中組成一個完整的Authentication對象�����,共其它組件共享。
下一篇: 總結Spring Security之 關于授權,保護web和保護方法
參考:
Spring in Action
Spring Security學習總結: http://m.tkk7.com/redhatlinux/archive/2008/08/20/223148.html
Spring Security2 學習精講: http://www.javaeye.com/topic/319965