理解數據流
流一般分為輸入流(Input Stream)和輸出流(Output Stream)兩類,但這種劃分并不是絕對的。比如一個文件,當向其中寫數據時,它就是一個輸出流;當從其中讀取數據時,它就是一個輸入流。當然,鍵盤只是一個數人流,而屏幕則只是一個輸出流。
字節流:
從InputStream和OutputStream派生出來的一系列類。這類流以字節(byte)為基本處理單位。
? InputStream、OutputStream
? ◇ FileInputStream、FileOutputStream
? ◇ PipedInputStream、PipedOutputStream
? ◇ ByteArrayInputStream、ByteArrayOutputStream
? ◇ FilterInputStream、FilterOutputStream
? ◇ DataInputStream、DataOutputStream
? ◇ BufferedInputStream、BufferedOutputStream
字符流:
從Reader和Writer派生出的一系列類,這類流以16位的Unicode碼表示的字符為基本處理單位
? Reader、Writer
? ◇ InputStreamReader、OutputStreamWriter
? ◇ FileReader、FileWriter
? ◇ CharArrayReader、CharArrayWriter
? ◇ PipedReader、PipedWriter
? ◇ FilterReader、FilterWriter
? ◇ BufferedReader、BufferedWriter
? ◇ StringReader、StringWriter
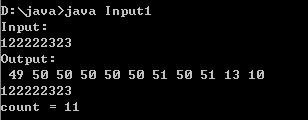
例子1
import java.io.*;
public class Input1
{
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
System.out.println("Input: ");
byte buffer[] = new byte[512]; //輸入緩沖區
int count = System.in.read(buffer); //讀取標準輸入流
System.out.println("Output: ");
for (int i=0;i<count;i++) //輸出buffer元素值
{
System.out.print(" "+buffer[i]);
}
System.out.println();
for (int i=0;i<count;i++) //按字符方式輸出buffer
{
System.out.print((char) buffer[i]);
}
System.out.println("count = "+ count); //buffer實際長度
}
}
運行結果:
例子2:
public class Input2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String Str=args[0];
String Str1=args[1];
int tempInt=Integer.parseInt(Str);
int tempInt1=Integer.parseInt(Str1);
tempInt *=2;
tempInt1*=3;
System.out.println(tempInt);
System.out.println(tempInt1);
}
}
運行結果

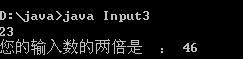
例子3:
import java.io.*;
public class Input3
{
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in =new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String s;
while((s = in.readLine()).length() != 0)
{
int i=Integer.parseInt(s);
System.out.println("您的輸入數的兩倍是 : " + i*2);
}
}
} //存在一個問題沒有退出
運行結果
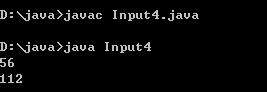
例子4:
public class Input4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte[] buf = new byte[256];
try {
// input
String str="";
do{
int c = System.in.read(buf,0,buf.length);
str += new String(buf,0,c);
} while(System.in.available()>0) ;
str = str.substring(0,str.length()-1); // remove the last return
int v = Integer.parseInt(str.trim());
System.out.println(""+v*2);
}
catch(Exception e)
{e.printStackTrace();}
}
}
運行結果
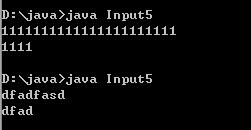
例子5 :
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Input5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bs = new BufferedInputStream(System.in);
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(bs);
byte[] b = new byte[4];//讀取前四位
dis.read(b);
System.out.println(new String(b,"gbk"));
dis.close();
}
}
運行結果: