|
|
Posted on 2010-08-31 01:11 penngo 閱讀(5167) 評論(4) 編輯 收藏 所屬分類: JBPM

前兩篇:
jbpm流程設計器(1)
jbpm流程設計器(2)
在這一篇已經實現了流程的保存與打開,下面看代碼
首先寫一個鏈表類來記錄繪制流程圖時的流程定義
 package com.workflow.designer.util; package com.workflow.designer.util;

 import java.io.Serializable; import java.io.Serializable;
 import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.ArrayList;
 import java.util.Hashtable; import java.util.Hashtable;
 import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Iterator;
 import java.util.List; import java.util.List;
 import java.util.Map; import java.util.Map;
 import java.util.Map.Entry; import java.util.Map.Entry;

  public class FlowProperty implements Serializable public class FlowProperty implements Serializable { {
 private String type = null; //記錄節點名 private String type = null; //記錄節點名
 private List<FlowProperty> child = null; //記錄子節點 private List<FlowProperty> child = null; //記錄子節點
 private Map<String, String> property = null; //節點屬性 private Map<String, String> property = null; //節點屬性

  public FlowProperty(String type) public FlowProperty(String type) { {
 this.type = type; this.type = type;
 this.child = new ArrayList<FlowProperty>(); this.child = new ArrayList<FlowProperty>();
 this.property = new Hashtable<String, String>(); this.property = new Hashtable<String, String>();
 } }

  public void addChild(FlowProperty fp) public void addChild(FlowProperty fp) { {
 child.add(fp); child.add(fp);
 } }

  public List<FlowProperty> getChild() public List<FlowProperty> getChild() { {
 return child; return child;
 } }

  public void addProperty(String key, String value) public void addProperty(String key, String value) { {
 property.put(key, value); property.put(key, value);
 } }

  public String getProperty(String key) public String getProperty(String key) { {
 return property.get(key); return property.get(key);
 } }

 //把類轉為jpdl的流程定義文本 //把類轉為jpdl的流程定義文本
  public String toJpdl() public String toJpdl() { {
 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
 sb.append("<").append(type); sb.append("<").append(type);
 Iterator<Entry<String, String>> it = property.entrySet().iterator(); Iterator<Entry<String, String>> it = property.entrySet().iterator();
  while(it.hasNext()) while(it.hasNext()) { {
 sb.append(" "); sb.append(" ");
 Entry<String, String> e = it.next(); Entry<String, String> e = it.next();
 sb.append(e.getKey()).append("=\"").append(e.getValue()).append("\""); sb.append(e.getKey()).append("=\"").append(e.getValue()).append("\"");
 } }
  if(child.size() > 0) if(child.size() > 0) { {
 sb.append(">\n"); sb.append(">\n");
  for(FlowProperty fp:child) for(FlowProperty fp:child) { {
 sb.append(fp.toJpdl()); sb.append(fp.toJpdl());
 } }
 sb.append("\n</").append(type).append(">"); sb.append("\n</").append(type).append(">");
 } }
  else else { {
 sb.append(" />"); sb.append(" />");
 } }
 return sb.toString(); return sb.toString();
 } }

  public String getType() public String getType()  { {
 return type; return type;
 } }

  public String toString() public String toString() { {
 return this.getProperty("name") == null ? "" : getProperty("name"); return this.getProperty("name") == null ? "" : getProperty("name");
 } }
 } }
把屬性保存在流程節點:
jgraphx的節點類只有一種mxCell,無論線條還是方形、端點,它都是mxCell。mxCell有個方法setValue(Object value)設置mxCell的值,而value的toString()的內容,就是節點顯示的文本,我們主要是把流程節點的屬性通過setValue方法記錄在mxCell上,修改之前的com.workflow.designer.view.GraphView類
  public class GraphView extends GraphImpl public class GraphView extends GraphImpl { {
  

  public void inser(Point p, Node n) public void inser(Point p, Node n) { {
 this.getGraph().getModel().beginUpdate(); this.getGraph().getModel().beginUpdate();
  try try { {
 //調用jgraph插入節點 //調用jgraph插入節點
 Object v1 = graph.insertVertex(parent, null, n.getLabel(), p.getX() - 5, p.getY() - 5, n.getWidth(), Object v1 = graph.insertVertex(parent, null, n.getLabel(), p.getX() - 5, p.getY() - 5, n.getWidth(),
 n.getHeight(), n.getShape()); n.getHeight(), n.getShape());
 mxCell cell = (mxCell)v1; mxCell cell = (mxCell)v1;
 mxGeometry g = cell.getGeometry(); mxGeometry g = cell.getGeometry();
 Rectangle r = g.getRectangle(); Rectangle r = g.getRectangle();
 cell.setConnectable(false); cell.setConnectable(false);
 FlowProperty fp = new FlowProperty(n.getType()); FlowProperty fp = new FlowProperty(n.getType());
 fp.addProperty("name", n.getLabel()); fp.addProperty("name", n.getLabel());
 fp.addProperty("g", r.getX() + "," + r.getY() + "," + r.getWidth() + "," + r.getHeight()); fp.addProperty("g", r.getX() + "," + r.getY() + "," + r.getWidth() + "," + r.getHeight());
 cell.setValue(fp); cell.setValue(fp);
 } }
  finally finally { {
 graph.getModel().endUpdate(); graph.getModel().endUpdate();
 } }
 } }
  
 } }
把節點保存為流程jpdl文件實現類
 package com.workflow.designer.jpdl; package com.workflow.designer.jpdl;

 import java.io.File; import java.io.File;
 import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream;
 import java.io.Serializable; import java.io.Serializable;

 import com.mxgraph.model.mxCell; import com.mxgraph.model.mxCell;
 import com.mxgraph.view.mxGraph; import com.mxgraph.view.mxGraph;
 import com.workflow.designer.util.FlowProperty; import com.workflow.designer.util.FlowProperty;

  public class SaveJpdl implements Serializable public class SaveJpdl implements Serializable { {
 private mxGraph graph = null; private mxGraph graph = null;
 private String fileName = null; private String fileName = null;
  public SaveJpdl() public SaveJpdl() { {

 } }

  public void save(String fileName, mxGraph graph) public void save(String fileName, mxGraph graph) { {
 this.fileName = fileName; this.fileName = fileName;
 this.graph = graph; this.graph = graph;
 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
 sb.append("<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"GBK\"?>\n"); sb.append("<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"GBK\"?>\n");
 sb.append(this.toJpdl()); sb.append(this.toJpdl());
  try try { {
 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(fileName)); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(fileName));
 fos.write(sb.toString().getBytes("GBK")); fos.write(sb.toString().getBytes("GBK"));
 fos.flush(); fos.flush();
 fos.close(); fos.close();
 } }
  catch(Exception e) catch(Exception e) { {
 e.printStackTrace(); e.printStackTrace();
 } }
 } }

  private String toJpdl() private String toJpdl() { {
 Object parent = graph.getDefaultParent(); Object parent = graph.getDefaultParent();
 Object[] ocjectCells = graph.getChildCells(parent); Object[] ocjectCells = graph.getChildCells(parent);
 FlowProperty process = new FlowProperty("process"); FlowProperty process = new FlowProperty("process");
 process.addProperty("name", "process"); process.addProperty("name", "process");
 process.addProperty("xmlns", "http://jbpm.org/4.4/jpdl"); process.addProperty("xmlns", "http://jbpm.org/4.4/jpdl");
  for(Object objectCell:ocjectCells) for(Object objectCell:ocjectCells) { {
  if(objectCell instanceof mxCell) if(objectCell instanceof mxCell) { {
 mxCell cell = (mxCell)objectCell; mxCell cell = (mxCell)objectCell;
  if(cell.isEdge() == false) if(cell.isEdge() == false) { {
 Object objectValue = cell.getValue(); Object objectValue = cell.getValue();
  if(objectValue != null && objectValue instanceof FlowProperty) if(objectValue != null && objectValue instanceof FlowProperty) { {
 FlowProperty flowNode = (FlowProperty)objectValue; FlowProperty flowNode = (FlowProperty)objectValue;
 process.addChild(flowNode); process.addChild(flowNode);
 } }
 } }
 } }
 } }
 return process.toJpdl(); return process.toJpdl();
 } }
 } }
打開jpdl流程定義實現類
 package com.workflow.designer.jpdl; package com.workflow.designer.jpdl;

 import java.io.File; import java.io.File;
 import java.util.Hashtable; import java.util.Hashtable;
 import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Iterator;
 import java.util.List; import java.util.List;
 import java.util.Map; import java.util.Map;

 import org.dom4j.Attribute; import org.dom4j.Attribute;
 import org.dom4j.Document; import org.dom4j.Document;
 import org.dom4j.Element; import org.dom4j.Element;
 import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader; import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;

 import com.mxgraph.model.mxCell; import com.mxgraph.model.mxCell;
 import com.mxgraph.model.mxGeometry; import com.mxgraph.model.mxGeometry;
 import com.mxgraph.view.mxGraph; import com.mxgraph.view.mxGraph;
 import com.workflow.designer.model.FlowNode; import com.workflow.designer.model.FlowNode;
 import com.workflow.designer.model.Node; import com.workflow.designer.model.Node;
 import com.workflow.designer.util.FlowProperty; import com.workflow.designer.util.FlowProperty;
 import com.workflow.designer.util.Logger; import com.workflow.designer.util.Logger;
 import com.workflow.designer.util.ObjectXml; import com.workflow.designer.util.ObjectXml;

  public class OpenJpdl public class OpenJpdl  { {
 private mxGraph graph = null; private mxGraph graph = null;
 private String fileName = null; private String fileName = null;
  public OpenJpdl() public OpenJpdl() { {

 } }

  public void open(String fileName, mxGraph graph) public void open(String fileName, mxGraph graph) { {
 this.fileName = fileName; this.fileName = fileName;
 this.graph = graph; this.graph = graph;
 Object parent = graph.getDefaultParent(); Object parent = graph.getDefaultParent();
 graph.getModel().beginUpdate(); graph.getModel().beginUpdate();
  try try  { {
 File f = new File(fileName); File f = new File(fileName);
 SAXReader reader = new SAXReader(); SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
 Document doc = reader.read(f); Document doc = reader.read(f);
 Element root = doc.getRootElement(); Element root = doc.getRootElement();
 FlowProperty process = new FlowProperty("process"); FlowProperty process = new FlowProperty("process");
 parseJpdl(root, process); parseJpdl(root, process);
 List<FlowProperty> list = process.getChild(); List<FlowProperty> list = process.getChild();
 ObjectXml ox = new ObjectXml(); ObjectXml ox = new ObjectXml();
 Map<String, Object> cellMap = new Hashtable<String, Object>(); Map<String, Object> cellMap = new Hashtable<String, Object>();
  for(FlowProperty node:list) for(FlowProperty node:list) { {
 String type = node.getType(); String type = node.getType();
 Node n = ox.getNode(type); Node n = ox.getNode(type);
 String g = node.getProperty("g"); String g = node.getProperty("g");
 int[] r = toRectangle(g); int[] r = toRectangle(g);
 Object v = graph.insertVertex(parent, null, node, r[0], r[1], r[2], Object v = graph.insertVertex(parent, null, node, r[0], r[1], r[2],
 r[3], n.getShape()); r[3], n.getShape());
 cellMap.put(node.getProperty("name"), v); cellMap.put(node.getProperty("name"), v);
 } }

  for(FlowProperty node:list) for(FlowProperty node:list) { {
 List<FlowProperty> edges = node.getChild(); List<FlowProperty> edges = node.getChild();
  if(edges.size() > 0) if(edges.size() > 0) { {
 int size = edges.size(); int size = edges.size();
  for(int h = 0; h < size; h++) for(int h = 0; h < size; h++) { {
 FlowProperty edge = edges.get(0); FlowProperty edge = edges.get(0);
  if(edge.getType().equals("transition")) if(edge.getType().equals("transition")) { {
 Object s = cellMap.get(node.getProperty("name")); Object s = cellMap.get(node.getProperty("name"));
 Object t = cellMap.get(edge.getProperty("to")); Object t = cellMap.get(edge.getProperty("to"));
 Object v = graph.insertEdge(parent, null, "", s, t); Object v = graph.insertEdge(parent, null, "", s, t);
 edges.remove(edge); edges.remove(edge);
 } }
 } }
 } }
 } }
 //Logger.debug(process.toJpdl()); //Logger.debug(process.toJpdl());

  }catch (Exception e) }catch (Exception e)  { {
 e.printStackTrace(); e.printStackTrace();
 } }
  finally finally { {
 graph.getModel().endUpdate(); graph.getModel().endUpdate();
 } }
 } }
  private int[] toRectangle(String g) private int[] toRectangle(String g) { {
 int[] r ; int[] r ;
 String[] str = g.split(","); String[] str = g.split(",");
 r = new int[str.length]; r = new int[str.length];
  for(int i = 0; i < str.length; i++) for(int i = 0; i < str.length; i++) { {
 r[i] = Float.valueOf(str[i]).intValue(); r[i] = Float.valueOf(str[i]).intValue();
 } }
 return r; return r;
 } }
  public void parseJpdl(Element element, FlowProperty fp) public void parseJpdl(Element element, FlowProperty fp) { {
  for ( Iterator a = element.attributeIterator(); a.hasNext(); ) for ( Iterator a = element.attributeIterator(); a.hasNext(); )  { {
 Attribute attribute = (Attribute) a.next(); Attribute attribute = (Attribute) a.next();
 fp.addProperty(attribute.getName(), attribute.getValue()); fp.addProperty(attribute.getName(), attribute.getValue());
 } }
  for ( Iterator a = element.elementIterator(); a.hasNext(); ) for ( Iterator a = element.elementIterator(); a.hasNext(); )  { {
 Element e = (Element) a.next(); Element e = (Element) a.next();
 FlowProperty flowNode = new FlowProperty(e.getName()); FlowProperty flowNode = new FlowProperty(e.getName());
 parseJpdl(e, flowNode); parseJpdl(e, flowNode);
 fp.addChild(flowNode); fp.addChild(flowNode);
 } }
 } }

 } }
下面看效果
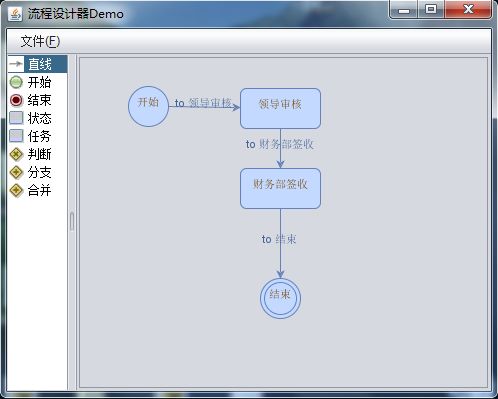
啥啥,畫完時才發現,居然連圖形的刪除功能都忘記沒有實現,一不小心畫錯了,就只能。。。。。。
生成的流程定義文件
 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="GBK"?> <?xml version="1.0" encoding="GBK"?>
 <process name="process" xmlns="http://jbpm.org/4.4/jpdl"> <process name="process" xmlns="http://jbpm.org/4.4/jpdl">
 <start name="開始" g="48.0,28.0,40.0,40.0"> <start name="開始" g="48.0,28.0,40.0,40.0">
 <transition name="to 領導審核" g="0.0,0.0" to="領導審核" /> <transition name="to 領導審核" g="0.0,0.0" to="領導審核" />
 </start> </start>
 <task name="領導審核" g="160.0,30.0,80.0,40.0"> <task name="領導審核" g="160.0,30.0,80.0,40.0">
 <transition name="to 財務部簽收" g="0.0,0.0" to="財務部簽收" /> <transition name="to 財務部簽收" g="0.0,0.0" to="財務部簽收" />
 </task> </task>
 <task name="財務部簽收" g="160.0,110.0,80.0,40.0"> <task name="財務部簽收" g="160.0,110.0,80.0,40.0">
 <transition name="to 結束" g="0.0,0.0" to="結束" /> <transition name="to 結束" g="0.0,0.0" to="結束" />
 </task> </task>
 <end name="結束" g="180.0,220.0,40.0,40.0" /> <end name="結束" g="180.0,220.0,40.0,40.0" />
 </process> </process>jgraphx可以直接生成圖片的,只是本人一時找不到哪一個方法是生成圖片的。。。。。。要實現生成圖片,請自行閱讀API
一般開發流程設計器都是為了簡化流程的開發,對于非常非常復雜的流程或者對于客戶(非開發人員)來說,提供可視化的流程流程設計器比手工寫流程定義效率和準確性高很多;不多說,還是自己慢慢體會。
設計器的文章介紹完畢,有興趣的朋友自己繼續深入研究。另外jgraphx還提供了javascript版,有興趣的可以自行研究使用javascript版開發流程設計器。
后段有時間的話,會寫點jbpm4.4入門類的文章或其它。
附件:jgraphxflow.jar.rar
評論
# re: jbpm流程設計器開發(3) 回復 更多評論
2010-12-13 12:43 by
在這一篇已經實現了流程的保存與打開,下面看代碼
# re: jbpm流程設計器開發(3)[未登錄] 回復 更多評論
2010-12-14 17:21 by
有源碼下載嗎?沒看到呀
# re: jbpm流程設計器開發(3) 回復 更多評論
2013-07-02 10:51 by
有點麻煩,試試ProcessOn
# re: jbpm流程設計器開發(3) 回復 更多評論
2014-08-05 15:17 by
受累能不能把源碼分享一下,讓大家學習學習
|